Welcome, educators! Whether you’ve been in the teaching world for a while or you’re just about to dive in, one thing is for sure: crafting engaging and effective lesson plans is a vital part of your job. That’s where Bloom’s Taxonomy Verbs come to help; it’s a toolkit that every teacher should be equipped with, as it pinpoints six crucial milestones in your student’s learning.
Read on and dive into over 200 Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs that can change the way you frame learning objectives and guide students toward success!
Understanding Bloom’s Taxonomy

Before we unleash the power of these verbs, a quick refresher on Bloom’s Taxonomy is in order. This hierarchical model categorizes learning objectives into six levels: Remember, Understand, Apply, Analyze, Evaluate, and Create. Each level represents a step in the cognitive development ladder, as they are crucial building blocks in your student’s comprehensive learning experiences.
Check out this blog post for a handy guide on common formative assessment questions to supercharge your Bloom's Taxonomy journey.
Why Use Bloom’s Taxonomy Verbs?
The purpose of using Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs is to precisely define and communicate the level of thinking or cognitive complexity required for a particular learning task or objective. Teachers can use these Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs in their lesson plans or communication in class to stimulate the right thinking skills. Here are more benefits of using Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs in your lessons:
- Clarity: They offer a clear roadmap for what you expect your students to achieve.
- Comprehensible outcomes: These verbs ensure objectives are specific and assessable.
- Better engagement: Using Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs in lesson communication involves the incorporating of a variety of cognitive skills, encouraging active participation and engagement.
- Diverse Assessment Opportunities: Design various assessment methods that cater to different levels of cognitive ability.
- Personalized Learning: Tailor teaching methods to cater to different learning styles and abilities.
200+ Bloom’s Taxonomy Verbs and Their Respective Categories
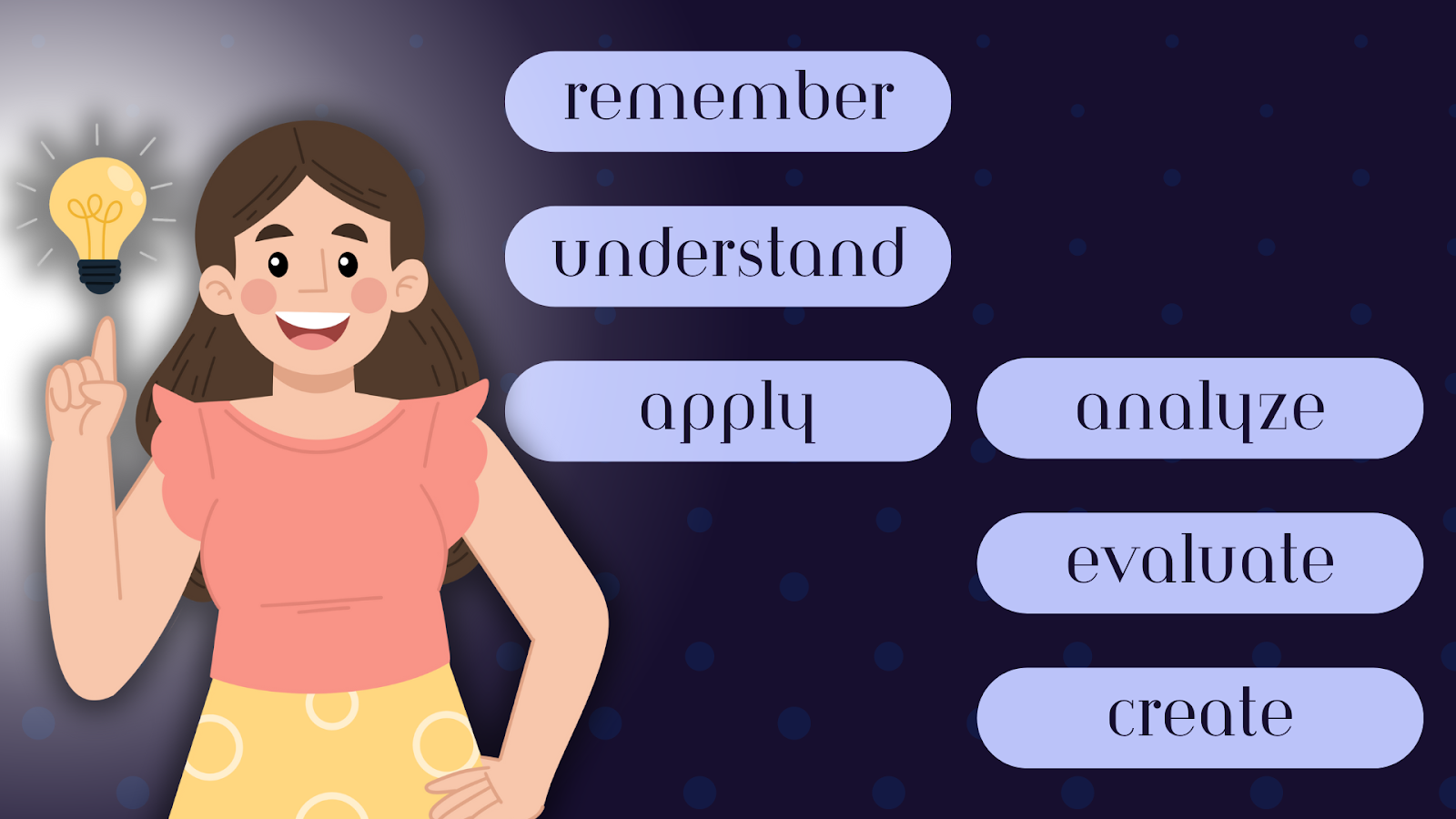
The taxonomy spans six cognitive levels: Remember, Understand, Apply, Analyze, Evaluate, and Create. Each level corresponds to specific verbs, guiding educators and learners alike in their journey as they develop a comprehensive approach to cognitive development.
Remember
The Remember category in Bloom’s Taxonomy Verbs highlights the vitality of fundamental cognitive processes such as recognizing, recalling, and retrieving information from memory. It is the first level in Bloom’s Taxonomy, the foundation for every higher-order thinking skill that follows.
As teachers, you are tasked to help your students hone this skill, so that it will help them later in life. This is important because learners are expected to recall information from memory and recognize key terms all throughout their lives.
Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs for the Remember category:
| Verb | Sentence |
| Cite | Cite two sources to support your argument in the essay. |
| Define | Define the term ‘ecosystem’ for your science project. |
| Describe | Describe the main character’s personality in the story. |
| Draw | Draw the structure of a plant cell in biology class. |
| Enumerate | Enumerate the steps involved in a chemical reaction. |
| Identify | Identify the countries on the map during geography class. |
| Index | Create an index for your term paper. |
| Indicate | Indicate the correct answer on the quiz. |
| Label | Label the parts of the human digestive system. |
| List | List the ingredients needed for the recipe. |
| Match | Match each word to its definition. |
| Meet | Meet the criteria outlined in the assignment guidelines. |
| Name | Name the capitals of five European countries. |
| Outline | Outline the main points of your presentation. |
| Point | Point to the area most affected by deforestation. |
| Quote | Quote a famous author to start your essay. |
| Read | Read the next chapter of the textbook for homework. |
| Recall | Recall the important dates from the history lecture. |
| Recite | Recite the poem you memorized for the class. |
| Recognize | Recognize the flags of different nations in the quiz. |
| Record | Record the observations from your experiment. |
| Repeat | Repeat the French phrases to improve pronunciation. |
| Reproduce | Reproduce the painting technique demonstrated by the teacher. |
| Review | Review the notes from today’s lecture. |
| Select | Select the correct option in the multiple-choice test. |
| State | State your hypothesis in the science report. |
| Study | Study the causes of the First World War. |
| Tabulate | Tabulate the survey results in a spreadsheet. |
| Trace | Trace the evolution of language in ancient civilizations. |
| Write | Write a summary of the documentary you watched. |
Understand
The Understand category in Bloom’s Taxonomy Chart Verbs, represents a cognitive level one step higher than remembering. Your students will understand with these verbs, meaning they will grasp the meaning of information rather than simply recalling it.
This skill is especially useful in comprehending concepts, interpreting ideas, and summarizing information in one’s own words. When you task your students to, for example, compare one thing with another, they demonstrate the ability to explain the significance of facts, describe relationships between concepts, and interpret information to create a cohesive understanding.
Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs for the Understand category:
| Verb | Sentence |
| Add | Add more examples to clarify your point. |
| Approximate | Approximate the total cost of your shopping list. |
| Articulate | Articulate your thoughts clearly during the presentation. |
| Associate | Associate the historical events with their causes. |
| Characterize | Characterize the protagonist’s role in the novel. |
| Clarify | Clarify the instructions before starting the experiment. |
| Classify | Classify these animals based on their habitat types. |
| Compare | Compare the two theories and note the differences. |
| Compute | Compute the total area of the land parcel. |
| Contrast | Contrast the economic policies of the two countries. |
| Convert | Convert the measurements from imperial to metric. |
| Defend | Defend your thesis statement with adequate evidence. |
| Describe | Describe the process of photosynthesis in plants. |
| Detail | Detail the steps you followed in the experiment. |
| Differentiate | Differentiate between qualitative and quantitative research. |
| Discuss | Discuss the implications of this study for future research. |
| Distinguish | Distinguish the symptoms of these two diseases. |
| Elaborate | Elaborate on your plan for the project. |
| Estimate | Estimate the time required to complete the task. |
| Example | Provide an example to illustrate this concept. |
| Explain | Explain how the machine operates. |
| Express | Express your ideas on the topic. |
| Extend | Extend your essay to cover all aspects of the question. |
| Extrapolate | Extrapolate the data to predict future trends. |
| Factor | Factor in all variables when solving the problem. |
| Generalize | Generalize the findings to a broader context. |
| Give | Give reasons for your choice. |
| Infer | Infer the author’s intent behind this statement. |
| Interact | Interact with the software to understand its features. |
| Interpolate | Interpolate to find the missing value. |
| Interpret | Interpret the results of the experiment. |
| Observe | Observe the reaction and record your findings. |
| Paraphrase | Paraphrase the paragraph in your own words. |
| Picture graphically | Picture graphically the rise and fall in temperature. |
| Predict | Predict the outcome of the election. |
| Review | Review the document for any errors. |
| Rewrite | Rewrite the passage to improve clarity. |
| Subtract | Subtract the expenses from your total income. |
| Summarize | Summarize the main points of the lecture. |
| Translate | Translate the paragraph into Spanish. |
| Visualize | Visualize the structure of the molecule. |
Apply
The Apply category in Bloom’s Taxonomy Verbs signifies a cognitive level where learners are equipped with the ability to use their knowledge in practical, real-life scenarios. At a stage like this, understanding transitions into action. Students are then able to apply concepts, theories, and methodologies to overcome obstacles, solve problems, and address everyday challenges.
Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs for the Apply category:
| Verb | Sentence |
| Acquire | Students need to acquire new skills for the project. |
| Adapt | They will adapt their strategies to solve complex problems. |
| Allocate | Allocate resources effectively for the group assignment. |
| Alphabetize | The librarian taught students to alphabetize books. |
| Apply | Apply the learned theory to real-world scenarios. |
| Ascertain | Ascertain the main idea from the text. |
| Assign | The teacher will assign roles for the class play. |
| Attain | They aim to attain proficiency in math. |
| Avoid | Avoid common errors while coding. |
| Back up | Always back up your research data. |
| Calculate | Calculate the area of the triangle. |
| Capture | Capture key points from the lecture. |
| Change | Change the variables to observe different outcomes. |
| Classify | Classify these chemicals based on their properties. |
| Compute | Compute the final scores from the test results. |
| Contrast | Contrast the two historical periods in your essay. |
| Convert | Convert the measurements from ounces to grams. |
| Defend | Defend your hypothesis in the science fair. |
| Describe | Describe the process of photosynthesis. |
| Detail | Detail the steps involved in the experiment. |
| Differentiate | Differentiate between renewable and non-renewable resources. |
| Discern | Discern the main themes in the novel. |
| Discover | Discover new methods to approach the problem. |
| Employ | Employ various techniques to improve your writing. |
| Exercise | Exercise caution while conducting experiments. |
| Experiment | Experiment with different colors in your art project. |
| Explore | Explore various cultures in your geography class. |
| Express | Express your opinions in the debate. |
| Extract | Extract the key information from the article. |
| Generalize | Generalize the findings from the survey. |
| Handle | Handle the laboratory equipment carefully. |
| Illustrate | Illustrate your answer with relevant examples. |
| Implement | Implement the new protocol in the study. |
| Incorporate | Incorporate feedback into your next draft. |
| Interconvert | Interconvert the units for international standards. |
| Interpolate | Interpolate missing data in the chart. |
| Interpret | Interpret the poem’s deeper meaning. |
| Manipulate | Manipulate the data to create a graph. |
| Modify | Modify your hypothesis based on the findings. |
| Operate | Operate the new software for the project. |
| Personalize | Personalize your learning approach in the course. |
| Plot | Plot the novel’s climax on the story arc. |
| Portray | Portray a historical character in the play. |
| Practice | Practice your presentation multiple times. |
| Predict | Predict the outcome of the experiment. |
| Prepare | Prepare a summary of the chapter. |
| Price | Price the products for the economics assignment. |
| Process | Process the survey data for analysis. |
| Produce | Produce a short film for the competition. |
| Program | Program a simple game using coding skills. |
| Project | Project your findings on the screen. |
| Provide | Provide examples to support your theory. |
| Relate | Relate the event to historical contexts. |
| Round off | Round off the figures for simplicity. |
| Sequence | Sequence the events in chronological order. |
| Show | Show how to solve the equation. |
| Simulate | Simulate a business scenario in class. |
| Sketch | Sketch the design for your art project. |
| Solve | Solve complex puzzles in the game. |
| Subscribe | Subscribe to the theory after thorough research. |
| Tabulate | Tabulate the results in a spreadsheet. |
| Transcribe | Transcribe the interview for the project. |
| Translate | Translate the document into another language. |
| Use | Use the microscope to observe the cells. |
Analyze
In the Analyze category in Bloom’s Taxonomy, learners will know more about the structure of information, breaking it down into constituent parts and discerning relationships. It is at a stage like this that individuals go beyond what they know and learn to be critical thinkers.
You can indulge your students in activities within the “Analyze” level by teaching them to compare, contrast, categorize, and discern cause-and-effect relationships.
Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs for the Analyze category:
| Action | Sentence |
| Analyze | When you analyze the data, look for patterns and trends that can inform your decision-making process. |
| Compare | Please compare the two solutions and identify their strengths and weaknesses. |
| Classify | It’s essential to classify the organisms correctly based on their genetic characteristics. |
| Contrast | Contrast the main themes of the two novels to highlight their differences. |
| Distinguish | Distinguish between the various species of birds based on their distinct features. |
| Infer | From the evidence presented, we can infer that the experiment was successful. |
| Separate | Separate the mixed substances into their individual components using the provided tools. |
| Explain | Take a moment to explain your reasoning behind choosing this particular approach. |
| Select | Select the appropriate tools for the task at hand to ensure efficiency. |
| Categorize | Categorize the different types of rocks based on their geological characteristics. |
| Connect | Connect the concepts learned in class to real-world applications for a deeper understanding. |
| Differentiate | Differentiate between the primary and secondary sources in your research. |
| Divide | Divide the project into manageable tasks to facilitate a more organized workflow. |
| Order | Order the elements in the periodic table based on their atomic numbers. |
| Prioritize | Prioritize the tasks on your to-do list to focus on the most important ones first. |
| Survey | Survey the participants to gather feedback on their overall experience. |
| Calculate | Use the formula to calculate the velocity of the moving object. |
| Conclude | After analyzing the data, conclude with a summary of your findings. |
| Correlate | Correlate the variables to determine if there is a significant relationship between them. |
| Deduce | From the given information, deduce the likely outcome of the experiment. |
| Devise | Devise a strategy to address the challenges identified during the planning phase. |
| Diagram | Diagram the process to provide a visual representation of the workflow. |
| Dissect | Dissect the argument to identify its key components and underlying assumptions. |
| Estimate | Estimate the total cost of the project based on the provided budget constraints. |
| Evaluate | Evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed solution in solving the problem. |
| Experiment | Design and conduct an experiment to test the hypothesis. |
| Focus | Focus on the main ideas to avoid getting lost in the details. |
| Illustrate | Use examples to illustrate the concept and enhance understanding. |
| Organize | Organize the information in a logical sequence for better clarity. |
| Outline | Outline the main points of your presentation before starting to ensure a coherent structure. |
| Plan | Plan your approach carefully to ensure a successful implementation. |
| Question | Encourage students to question the assumptions underlying the theory. |
| Test | Test the hypothesis through controlled experiments to validate your findings. |
Evaluate
The Evaluate category in Bloom’s Taxonomy focuses on a cognitive level where students engage in critical thinking and engage in judgment of information. At this stage, students scratch their heads as they evaluate the validity, credibility, and relevance of new or old ideas, theories, or solutions.
In this level, students will weigh evidence, consider a situation from multiple perspectives, and form well-supported conclusions.
Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs for the Evaluate category:
| Verb | Sentence |
| Appraise | Appraise the value of the old painting in your report. |
| Assess | Assess the outcomes of the marketing campaign. |
| Audit | Audit the company’s financial records for accuracy. |
| Blueprint | Blueprint a strategy for the new business model. |
| Compare | Compare the two novels for your literature assignment. |
| Conclude | Conclude your essay with a strong summary of the arguments. |
| Contrast | Contrast classical and modern art in your presentation. |
| Counsel | Counsel the client on the best legal approach. |
| Criticize | Criticize the methodologies used in the research study. |
| Defend | Defend your thesis against the panel’s questions. |
| Detect | Detect any anomalies in the data set. |
| Diagnose | Diagnose the cause of the technical malfunction. |
| Discriminate | Discriminate between fact and opinion in the news articles. |
| Estimate | Estimate the project’s completion time. |
| Evaluate | Evaluate the effectiveness of the new policy. |
| Explain | Explain your reasoning for the chosen solution. |
| Grade | Grade the students’ assignments fairly. |
| Hire | Hire the most qualified candidate for the job. |
| Interpret | Interpret the implications of the survey results. |
| Judge | Judge the contest entries on their originality. |
| Justify | Justify your decision to pursue a different approach. |
| Measure | Measure the success of the event. |
| Predict | Predict the trends for the coming year. |
| Prescribe | Prescribe a course of action for the problem. |
| Rank | Rank the candidates based on their qualifications. |
| Rate | Rate the service from one to ten. |
| Recommend | Recommend the best course of treatment. |
| Release | Release your findings to the public. |
| Select | Select the most relevant information for your report. |
| Summarize | Summarize the main points of the argument. |
| Support | Support your claims with evidence. |
| Test | Test the hypothesis with a controlled experiment. |
| Validate | Validate the authenticity of the historical document. |
| Verify | Verify the accuracy of the information provided. |
Create
Finally, the highest cognitive level in Bloom’s Taxonomy – Create. This category pushes learners to generate original ideas, products, and solutions. With these verbs and your help, your students will transcend previous knowledge, combining and synthesizing information to produce something completely new.
Mastering this level demonstrates a profound comprehension of content and the ability to apply knowledge in a creative manner.
Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs for the Create category:
| Verb | Sentence |
| Abstract | Students were asked to abstract the main concepts from the lecture. |
| Animate | The assignment was to animate a short story using digital tools. |
| Arrange | Arrange the musical notes to create a harmonious melody. |
| Assemble | The students will assemble their robotics projects next week. |
| Budget | Budget your resources effectively for the event planning project. |
| Categorize | Categorize the artifacts in the museum exhibit. |
| Code | Code a simple program to solve the math problem. |
| Combine | Combine different genres to create a unique piece of writing. |
| Compile | Compile your research into a comprehensive report. |
| Compose | Compose a poem about your childhood memories. |
| Construct | Construct a model of a sustainable house using recycled materials. |
| Cope | Design a strategy to cope with stress during exams. |
| Correspond | Create an artwork that corresponds with the theme of nature. |
| Create | Create a marketing campaign for a new product. |
| Cultivate | Cultivate a garden in the schoolyard as part of a biology project. |
| Debug | Debug the code to improve the software’s functionality. |
| Depict | Depict the historical event in a vivid painting. |
| Design | Design a website for the school’s annual cultural fest. |
| Develop | Develop a business plan for a startup company. |
| Devise | Devise a new method for recycling plastics. |
| Dictate | Dictate a story and turn it into an audiobook. |
| Enhance | Enhance the existing design to make it more user-friendly. |
| Explain | Explain a complex theory using a simple analogy. |
| Facilitate | Facilitate a workshop on creative writing techniques. |
| Format | Format the document to make it more visually appealing. |
| Formulate | Formulate a hypothesis for your science project. |
| Generalize | Generalize the study’s findings to apply to a wider population. |
| Generate | Generate a list of ideas for the group discussion. |
| Handle | Handle the project management to ensure timely completion. |
| Import | Import data from various sources for the research project. |
| Improve | Improve the process to increase efficiency. |
| Incorporate | Incorporate feedback from the survey into the new design. |
Adding Your Touch to Bloom’s Taxonomy: Key Tips
As you integrate these verbs into your lesson plans, remember:
- Be specific! Avoid using general verbs like ‘understand’ or ‘learn.’ For an enhanced effect, use precise verbs like ‘classify’ or ‘summarize.’
- Personalize! Mix and match verbs to your liking from different categories to cover a wide range of cognitive skills.
- Context is key. Align verbs with your lesson plans and to the appropriate cognitive level of your students.
- Incorporate Interactive Learning. Incorporate interactive elements such as interactive quizzes in your lesson that align with each Bloom’s Taxonomy levels to elevate engagement and participation in the classroom.
- Gamify Your Lesson! Combining gamification and Bloom’s Taxonomy teaching enhances learning outcomes by leveraging game elements to scaffold and reinforce different cognitive skills.
Pro Tip: Automate the process of classroom quiz generation based on Bloom's Taxonomy levels using ClassPoint AI - an AI designed to scan your PowerPoint content and create tailored questions based on Bloom's Taxonomy levels.
Final Thoughts
There you have it, teachers! The ultimate collection of Bloom’s Taxonomy Verbs, designed to enhance your teaching and your students’ learning.
By sprinkling these verbs to your lesson plan, you’ll empower your students to reach great milestones in their learning journey. Remember, teaching is an art, and with the right tools, you can create a masterpiece.
Ready to transform your teaching? Download the comprehensive list of Bloom’s Taxonomy Verbs and start crafting unique lesson objectives that inspire and challenge the students of tomorrow.

