So, you have decided to start an informal book club session with your pals or students that meet weekly to discuss and share ideas. But you are not sure where to start to create a book club experience that all of the participants actually look forward to the next session. The last thing you want is a book club where everyone comes in to chit chat about irrelevant things, or worse, do their homework or take naps.
This comprehensive book club questions guide is carefully put together and is specially tailored towards teachers and students on genres that are usually taught in schools. With this collection of book club questions, you will be well equipped to run an effective and engaging book club sessions that participants can’t wait to show up on time for the next one!
Benefits of Book Club Discussions
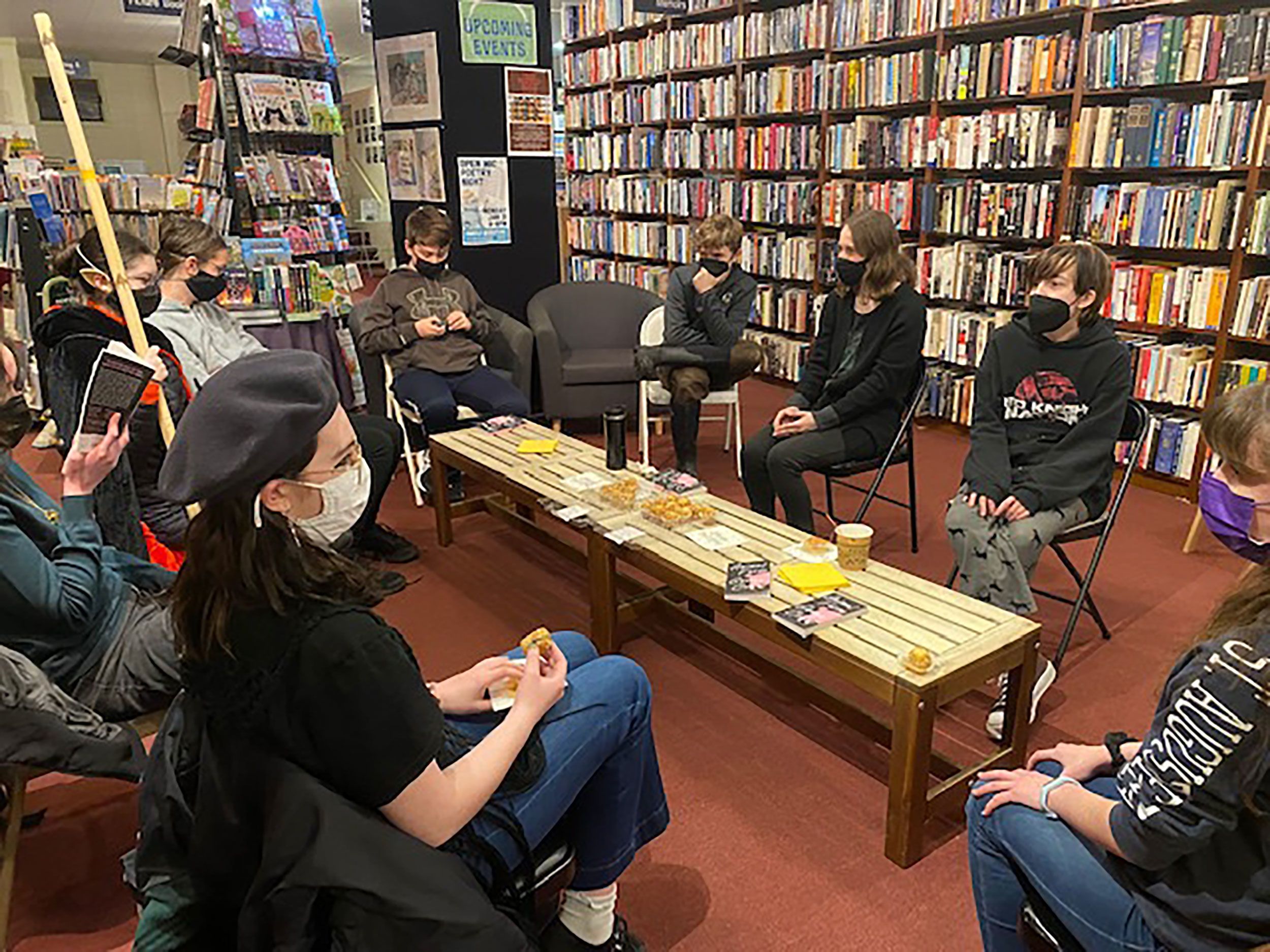

- Greater Appreciation for Literature: Regular discussion of books can deepen students’ appreciation for different genres, styles, and authors.
- Increased Reading Comprehension and Analytical Skills: Discussing books encourages deeper understanding and interpretation of texts, improving overall reading comprehension and analytical skills.
- Increased Vocabulary and Language Skills: Exposure to diverse language and literary styles enriches students’ vocabulary, language usage and writing skills.
- Enhanced Critical Thinking and Reflection: Engaging in discussions helps students analyze and evaluate different perspectives, reflecting on their own beliefs and fostering critical thinking and analytical skills.
- Improved Communication Skills: Regular participation in book club discussions helps students practice articulating their thoughts, listening actively, and responding thoughtfully.
- Development of Social-Emotional Skills: Book clubs provide a platform for collaborative learning, teamwork, and respectful debate, enhancing social interaction skills.
- Exposure to Diverse Perspectives: Book clubs often involve diverse participants, allowing students to encounter and appreciate different viewpoints and cultural contexts, encouraging open-mindedness and cultural responsiveness.
130+ Book Club Questions for All Genres in School
Fiction
Literary Fiction
Examples: “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee and “The Great Gatsby” by F. Scott Fitzgerald.

- How do the characters evolve throughout the story?
- What themes are prominent in the book, and how are they conveyed?
- How does the author’s writing style enhance or detract from the story?
- What role does the setting play in the narrative?
- How does the book’s structure affect your reading experience?
- Which character do you relate to the most and why?
- What is the significance of the book’s title?
- How do secondary characters influence the main character’s journey?
- What message or lesson did you take away from the story?
- How does the book address universal human experiences?
Historical Fiction
Examples: “The Book Thief” by Markus Zusak and “Number the Stars” by Lois Lowry.

- What are the key historical events that shape the plot and characters?
- How do the fictional elements of the story interact with the historical facts?
- What historical details stood out to you, and why?
- How do the characters’ actions reflect the social norms of their time?
- What did you learn about the historical period from reading the book?
- How does the author balance historical accuracy with creative storytelling?
- Which character’s perspective provided the most insight into the historical context?
- How does the setting influence the characters’ decisions and lives?
- What parallels can you draw between the events in the book and contemporary issues?
Science Fiction
Examples: “1984” by George Orwell and “Ender’s Game” by Orson Scott Card.

- What does the book suggest about the future of humanity?
- How does the setting influence the characters and plot?
- What ethical dilemmas are presented in the story?
- How do the characters adapt to the technological environment?
- What themes are explored through the science fiction elements?
- How does the book challenge your perception of reality and possibility?
- What impact does the advanced technology have on society in the book?
- How do the speculative elements enhance the narrative?
Fantasy
Examples: “Harry Potter” series by J.K. Rowling and “The Hobbit” by J.R.R. Tolkien.

- How does the world-building contribute to the overall story?
- What are the moral or ethical questions raised by the fantasy elements?
- How do the characters’ journeys reflect traditional heroic archetypes?
- What role do mythical creatures or beings play in the narrative?
- How does the setting influence the plot and character development?
- What themes are explored through the fantastical elements?
- How do the magical elements affect the characters’ lives and decisions?
- What parallels can you draw between the fantasy world and our own?
- How does the author create a sense of wonder and imagination?
Mystery/Thriller
Examples: “Sherlock Holmes” stories by Arthur Conan Doyle and “And Then There Were None” by Agatha Christie.

- How did the author create suspense and tension throughout the story?
- Were there any red herrings or misleading clues? How did they affect your reading experience?
- What motivations drive the characters’ actions?
- How do the setting and atmosphere contribute to the sense of mystery?
- What are the key clues that lead to the resolution?
- How do the characters’ relationships influence the unfolding of the plot?
- What twists and turns did you find most surprising?
- How does the author develop the antagonist?
- How does the book explore the themes of justice and morality?
Non-Fiction
Biography/Autobiography
Examples: “The Diary of a Young Girl” by Anne Frank and “Steve Jobs” by Walter Isaacson.

- What were the key moments in the subject’s life that shaped their character?
- How does the subject’s life reflect broader historical or social trends?
- What lessons can be learned from the subject’s experiences?
- How does the author portray the subject’s personal and professional life?
- What challenges did the subject face, and how did they overcome them?
- How did the subject’s background and upbringing influence their achievements?
- What were the most surprising or unexpected aspects of the subject’s life?
- How does the author balance objectivity and personal perspective?
- How does the subject’s story inspire or resonate with you personally?
Memoir
Examples: “I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings” by Maya Angelou and “Educated” by Tara Westover.

- How does the author’s personal perspective influence the narrative?
- What themes or messages are central to the memoir?
- How did the author’s background and experiences shape their worldview?
- What are the key events that the author focuses on, and why?
- How does the memoir reflect broader social or cultural issues?
- How does the author’s writing style contribute to the intimacy of the memoir?
- What emotions did the memoir evoke in you?
- How does the author handle memory and subjectivity in recounting their experiences?
- How does the memoir challenge or confirm your own perspectives on the topics discussed?
Informational Texts
Examples: “The Immortal Life of Henrietta Lacks” by Rebecca Skloot.

- How effectively does the author present complex information?
- How can the knowledge gained from this book be applied in real life?
- What evidence does the author use to support their claims?
- How does the book change or enhance your understanding of the topic?
- What are the key arguments or points made in the book?
- How does the author structure the book to facilitate understanding?
- What biases or assumptions does the author bring to the topic?
- How does the book compare to other works on the same subject?
- What questions do you still have after reading the book?
Essay and Speech
Examples: Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” and essays by Ralph Waldo Emerson.
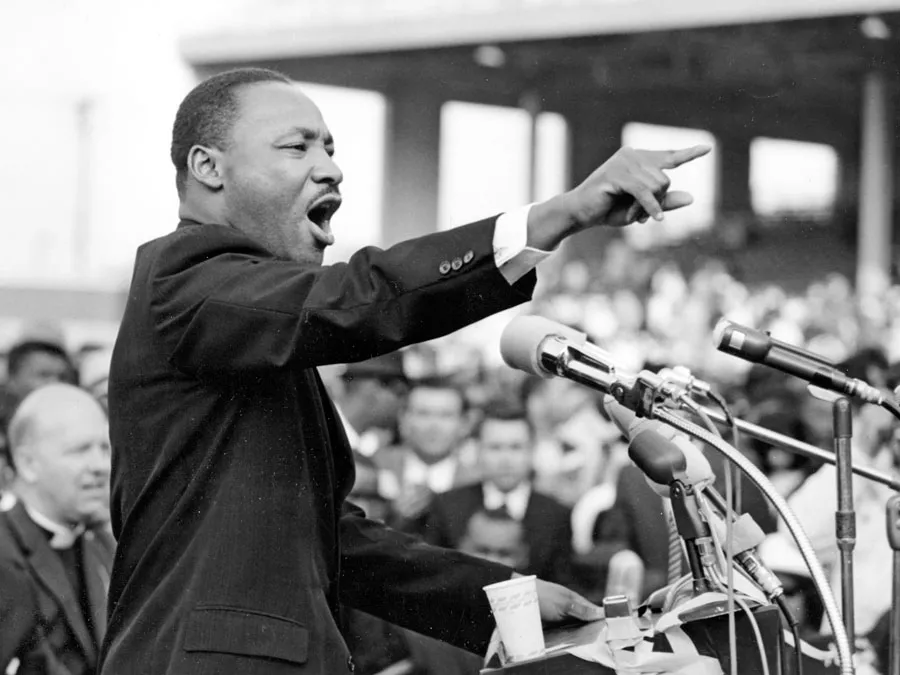

- What is the main argument or message of the essay/speech?
- How does the author use rhetoric and persuasion to convey their point?
- How relevant are the ideas presented in today’s context?
- How does the author’s background influence their perspective?
- What evidence or examples does the author use to support their claims?
- How does the structure of the essay/speech enhance its effectiveness?
- What emotions does the essay/speech evoke?
- How does the essay/speech challenge your existing beliefs or opinions?
- What rhetorical devices does the author use, and how effective are they?
Check out ways to manage classroom plagiarism effectively.
Poetry
Examples: “The Odyssey” or “The Iliad” by Homer

- What emotions does the poem evoke, and how does the poet achieve this?
- How does the poet’s use of language enhance the poem’s impact?
- How does the poem’s rhythm and meter contribute to its effect?
- How does the poem relate to the poet’s other works?
- What is the story being told, and how is it structured?
- How does the poet develop characters and settings within the poem?
- What themes are explored through the narrative?
- How does the poem’s form influence its storytelling?
- What is the climax of the narrative, and how is it resolved?
- What literary devices does the poet use to enhance the narrative?
Drama
Tragedy
Examples: “Macbeth” and “Hamlet” by William Shakespeare.

- How do the protagonist’s flaws contribute to their downfall?
- What is the role of fate versus free will in the story?
- How does the tragedy elicit a sense of catharsis?
- What are the key turning points in the plot?
- How do secondary characters influence the tragic outcome?
- How does the setting enhance the tragic elements of the story?
- What themes are explored through the tragedy?
- How does the playwright use dramatic irony?
- What emotions did the tragedy evoke in you?
- How does the tragedy reflect the time period in which it was written?
Comedy
Examples: “A Midsummer Night’s Dream” by William Shakespeare and “The Importance of Being Earnest” by Oscar Wilde.

- What social norms or conventions does the comedy challenge or satirize?
- How do humor and irony enhance the narrative?
- How do the characters’ interactions drive the comedic elements of the play?
- What are the main sources of conflict, and how are they resolved in a humorous way?
- How does the play use misunderstandings or mistaken identities for comedic effect?
- What role does satire play in the comedy?
- How does the comedic structure contribute to the play’s overall message?
- How do the characters’ personalities and quirks contribute to the humor?
- What are the most memorable comedic scenes, and why?
- How does the play address serious themes or social issues through humor?
Mythology and Folklore
Myths
Examples: Greek, Roman, and Norse myths.
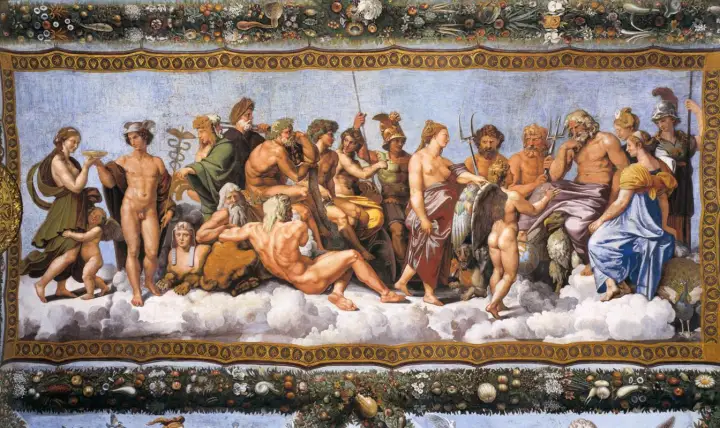

- What natural phenomena or cultural practices does the myth explain?
- How do the characters embody the values or flaws of the society that created them?
- How does the myth’s setting influence its narrative?
- What role do gods or supernatural beings play in the myth?
- What are the key moral or philosophical lessons of the myth?
- How does the myth reflect the beliefs and values of the culture from which it originates?
- How does the myth compare to other myths from different cultures?
- What symbols or archetypes are present in the myth, and what do they represent?
- How does the structure of the myth contribute to its storytelling?
- How do the characters’ fates and actions reflect the concept of fate or destiny in the myth?
Folktales
Examples: “Cinderella” and “Hansel and Gretel.”

- What moral or lesson is conveyed through the folktale?
- How do the characters and plot structure contribute to the story’s message?
- How does the folktale reflect the culture and values of its origin?
- What role do recurring motifs or symbols play in the folktale?
- What are the central conflicts in the folktale, and how are they resolved?
- How do the characters’ traits and actions reflect traditional cultural norms?
- What are the similarities and differences between this folktale and others you know?
- How does the folktale address themes of justice, morality, or human nature?
- What personal reflections or insights did you gain from the folktale?
Fables
Examples: Aesop’s Fables.

- What is the fable’s moral, and how is it conveyed through the story?
- How do the animal characters and their traits relate to human behavior?
- What makes the fable’s lesson relevant or applicable today?
- How does the use of allegory enhance the fable’s storytelling?
- What role does irony play in the fable?
- How do the fable’s characters interact to illustrate its moral?
- What are the main symbols or metaphors used in the fable?
- How does the fable compare to other fables in terms of theme and message?
- What impact did the fable’s moral have on your understanding of similar real-life situations?
Looking for more fun ways to engage with your students? Try these common sense questions and hot seat questions.
Download this list of book club questions as a PDF!
The Ultimate Book Club Questions List for Teachers and Students
Save them now for a successful and engaging book club discussion
7 Pro Tips to Run a Successful Book Club
Running a successful book club in a school involves careful planning, effective management, and engaging activities. Here are some tips to help ensure your book club thrives:
- Define the Purpose and Goals
- Clarify Objectives: Decide whether the club’s focus is on fostering a love for reading, enhancing literary analysis skills, or encouraging social interaction.
- Set Goals: Establish clear goals for what you want the book club to achieve, such as improved reading comprehension or increased student engagement.
- Choose the Right Books (Ideally, They are Connected to Curriculum)
- Link to Classes: Integrate book club discussions with classroom learning to reinforce educational content and skills.
- Cross-Disciplinary Themes: Choose books that tie into other subjects like history, science, or social studies to provide a broader context.
- Student Input: Allow students to have a say in book selections to increase their investment and enthusiasm.

- Schedule Regular Meetings
- Consistent Timing: Hold meetings at regular intervals, such as weekly or monthly, to maintain momentum.
- Flexible Timing: Consider students’ schedules and find a time that works for most participants, possibly during lunch or after school.
- Foster an Inclusive and Positive Environment
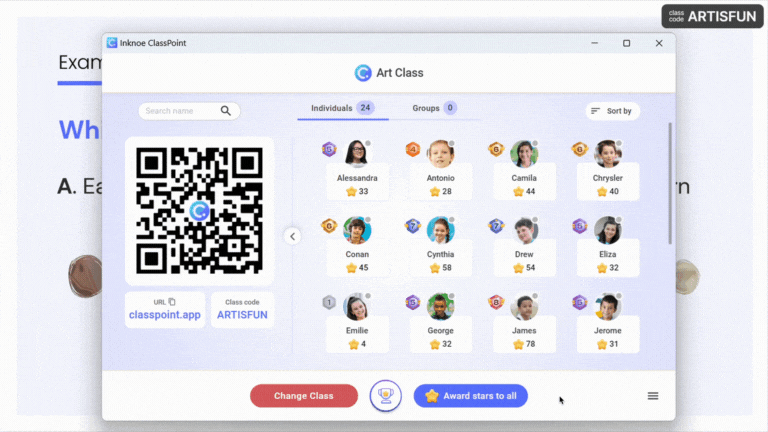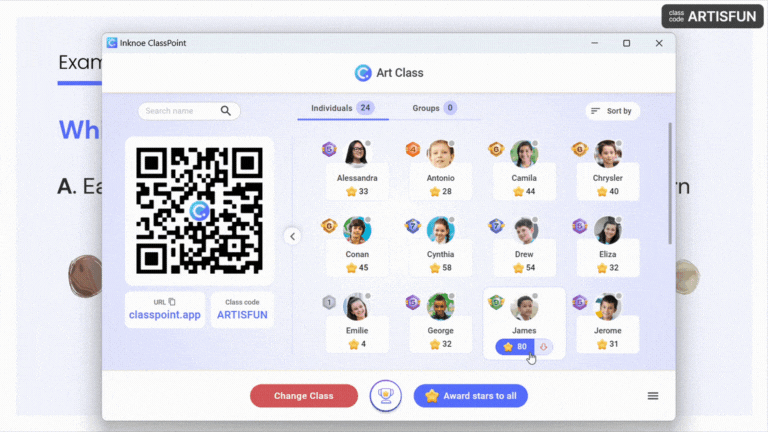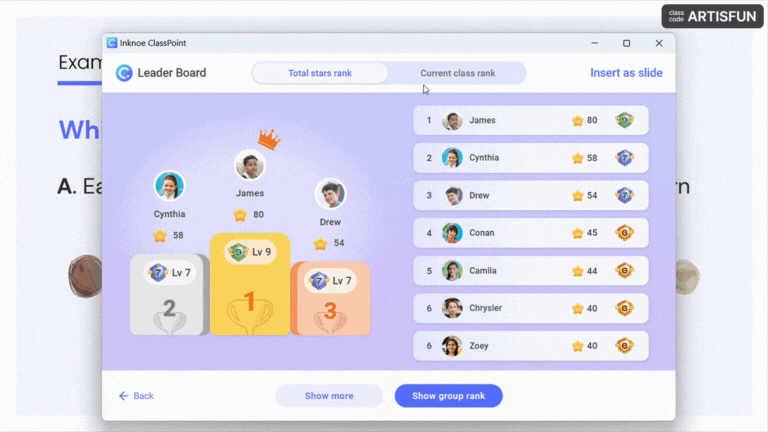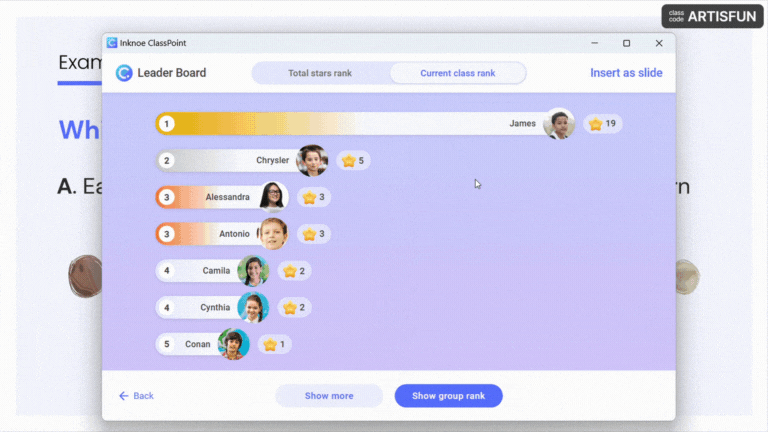
- Encourage Participation: Create a welcoming atmosphere where all students feel comfortable sharing their thoughts and opinions.
- Respect Diverse Views: Emphasize respect for differing perspectives and encourage open, constructive discussions.
- Celebrate Achievements: Recognize and celebrate milestones, such as finishing a challenging book or achieving a discussion goal.
Pro Tip: Award stars and points to participants who contribute and participate in every session and reveal the leaderboard at the end of a book club session to recognize these active participants.
- Incorporate Interactive Activities Into Book Club Questions
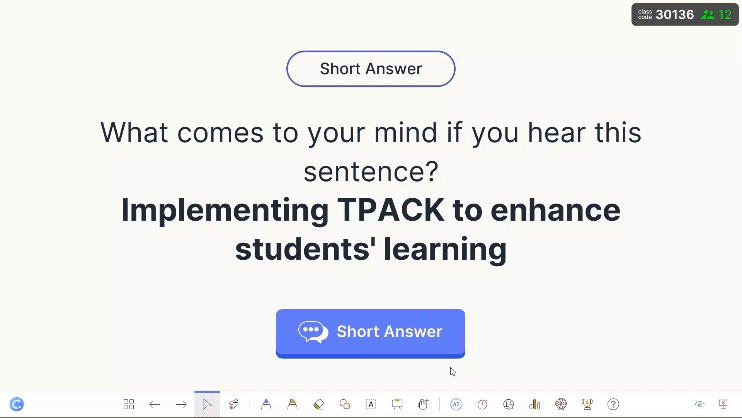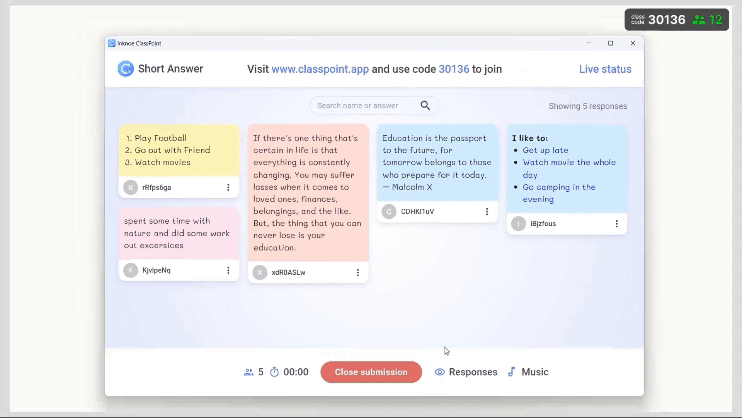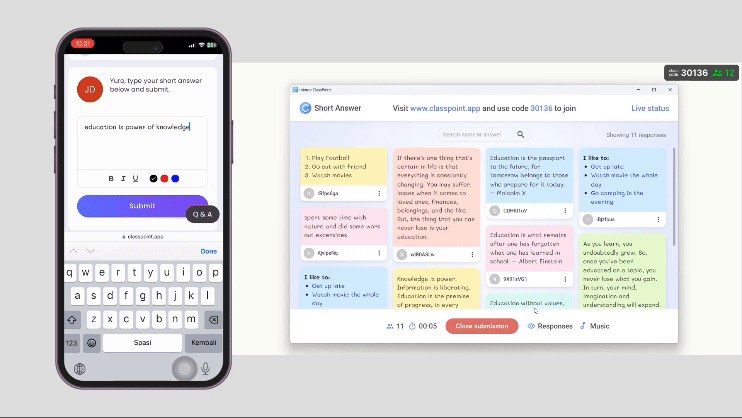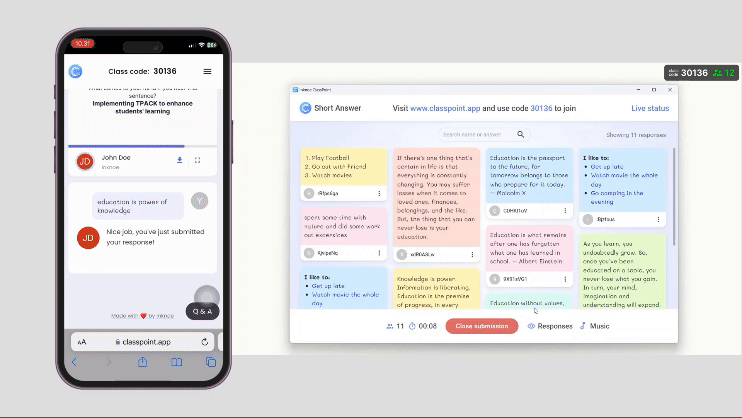
- Creative Projects: Include activities such as quizzes, art projects, creative writing assignments, or dramatic readings related to the book.
- Guest Speakers: Invite authors, local librarians, or experts to speak about the book or its themes.
Pro Tip: Run interactive quizzes or trivia from time to time to help consolidate learning while spicing up the book club discussion sessions.
- Evaluate and Adapt
- Feedback: Regularly seek feedback from students about what they enjoy and what could be improved.
- Adapt: Be willing to adjust book choices, discussion formats, or meeting times based on feedback and evolving interests.
- Leverage Technology
- Virtual Meetings: For students who cannot attend in person, consider virtual meetings or online discussion forums.
- Digital Tools: Use tools like interactive whiteboards or annotations to facilitate ongoing conversations.
Pro Tip: ClassPoint offers a rich diversity of interactive presentation tools in PowerPoint to make learning new concepts and ideas more memorable.
Final Thoughts
Ready to create an engaging and productive book club experience? By using our list of book club questions provided, you can spark meaningful conversations and foster a deeper understanding of the texts being read. Remember to encourage diverse perspectives and ensure that every participant has the opportunity to contribute. Don’t forget to add interactive experience and leverage technology to create a vibrant book club atmosphere where students are motivated to participate, share ideas, and look forward to each session!
There is no right and wrong way to running a book club; the key is to remain adaptable and responsive to the needs and interests of your participants. Ultimately, a successful book club is one that inspires a love of reading and learning, making each session a rewarding and anticipated event.
