Over the years, researchers have studied the Flynn Effect, which refers to the steady rise in IQ scores across generations. Now, with Gen Alpha—those born in the early 2010s and beyond—experts are wondering whether this trend will continue or take a different turn. The question of whether Gen Alpha will experience the same cognitive gains or face new challenges in an evolving world is still up for debate.
Could the rapid advancements in technology and changing social environments influence how this generation develops intellectually? While some data suggests fluctuations in IQ trends, it’s important to approach the topic with an open mind and consider all the factors at play.
The Flynn Effect and Gen Alpha: A Summarized Look at Intelligence Trends
The Flynn Effect refers to the observed increase in IQ scores across various populations over time, first identified by researcher James Flynn in the 1980s. This phenomenon suggests that the average IQ has steadily risen, with an estimated increase of about 3 points per decade since the early 20th century. As we look to the future with Gen Alpha, it’s crucial to explore whether these trends will continue or shift in response to new societal factors.

Historical Background of the Flynn Effect
James Flynn’s research, published in 1984, revealed a significant rise in IQ scores over several decades. Specifically, he identified a 13.8-point increase among Americans from 1932 to 1978, translating to an annual increase of approximately 0.3 IQ points.
The term Flynn Effect was later popularized by Richard Herrnstein and Charles Murray in their 1994 book The Bell Curve to encapsulate Flynn’s findings. Flynn himself suggested, however, that if individuals from a century ago were tested today, they would score significantly lower compared to present-day individuals.
Mechanisms Driving the Flynn Effect
Several environmental factors have been proposed to explain this consistent rise in IQ scores, with the following being the most prominent:
- Education: The quality and access to education have seen marked improvements over time, contributing to enhanced problem-solving abilities and cognitive skills.
- Nutrition: Improved nutrition has been linked to better cognitive development. Studies show that deficiencies in essential nutrients can negatively affect IQ, while better access to nutrition supports cognitive growth.
- Reduced Exposure to Toxins: Decreased exposure to harmful environmental toxins has likely contributed to improved cognitive function across generations.
- Cognitive Stimulation: The modern world offers increased engagement with technology and complex cognitive tasks, which may also play a role in elevating intelligence scores.
The Flynn Effect Gen Alpha Seems to Be Changing Pace From Previous Generations
While the Flynn Effect remained strong throughout the 20th century, recent studies suggest that it may be diminishing—or even reversing—in some developed countries since the late 1990s. Countries like Norway, Denmark, and the UK have reported declines in IQ scores, potentially due to cultural changes that make certain test items less relevant.
Despite these trends, the average IQ of recent generations, including Gen Alpha, is still higher than that of previous generations. This reflects the cumulative impact of improved education, better nutrition, and other environmental benefits. Flynn himself noted that contemporary individuals excel in solving abstract problems, a skill increasingly emphasized in modern education.
What Makes Gen Alpha Vulnerable to a Reverse Flynn Effect?
While previous generations have benefited from the steady rise in IQ scores, Gen Alpha faces unique challenges that may make them more susceptible to a potential reversal of the Flynn Effect. Various factors, from changing lifestyles to the rapid advancement of technology, could contribute to a shift in cognitive development patterns.
📱 The Impact of Technology and Screen Time
Gen Alpha is the first generation to grow up fully immersed in digital devices from birth. While this access to technology can enhance learning in many ways, the overstimulation from constant screen time poses risks. Studies show that excessive screen use can impact attention spans, memory retention, and even critical thinking skills.
| Factor | Potential Impact on Cognitive Development |
|---|---|
| Excessive screen time | Reduced attention span, lower problem-solving capabilities |
| Social media consumption | Shallow information processing, reduced face-to-face interactions |
| Digital multitasking | Difficulty focusing on single tasks, impaired memory recall |
🏫 Shifts in Education Priorities
Educational trends have shifted towards more project-based and collaborative learning, with a stronger focus on soft skills like communication and empathy. While these changes are valuable, they may reduce the emphasis on traditional cognitive tasks that IQ tests measure. In some regions, this could mean less practice in skills related to abstract problem-solving, which the Flynn Effect historically favored.
🏞️ Declining Physical Activity and Outdoor Play
The rise of digital entertainment has also led to a decline in physical activity and outdoor play among children, which can negatively affect cognitive development. Studies show that regular physical exercise enhances memory, concentration, and problem-solving skills in children. With Gen Alpha spending more time indoors and engaging in sedentary activities, they may miss out on these cognitive benefits.
🧠 Increased Mental Health Pressures
Modern societal pressures, including the rise of social media, academic expectations, and the pandemic’s long-lasting effects, have increased mental health concerns in Gen Alpha. Anxiety, depression, and stress during critical developmental years can hinder cognitive performance, particularly in areas like memory and learning speed.
Factors That Could Continue the Flynn Effect in Gen Alpha
Despite the challenges facing Gen Alpha, certain factors have the potential to sustain or even boost cognitive development, continuing the positive trends observed in previous generations. Here’s how these factors are contributing to cognitive growth:
1. Advancements in Personalized Learning
- Tailored Educational Approaches
Personalized learning technologies, such as adaptive learning platforms, allow for customization of educational experiences based on individual student needs and learning styles. This personalization helps address specific learning gaps and supports better academic outcomes.
If you're an educator who actively uses PowerPoint, considering adding ClassPoint to you teaching arsenal. With ClassPoint plugged right inside PowerPoint, you can turn your slides into instant interactive quizzes, make learning fun with gamification, access live slide show tools for dynamic presentations, and even use AI to generate quiz content on the spot!
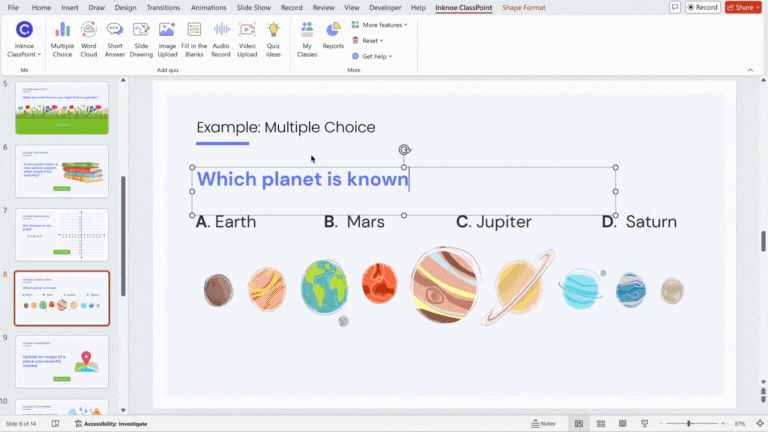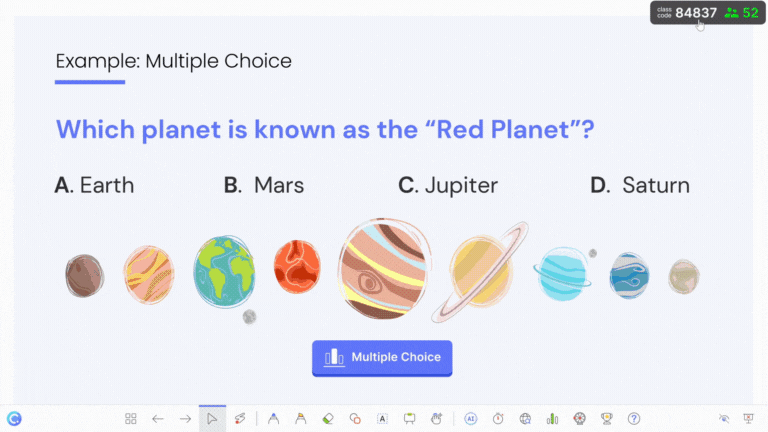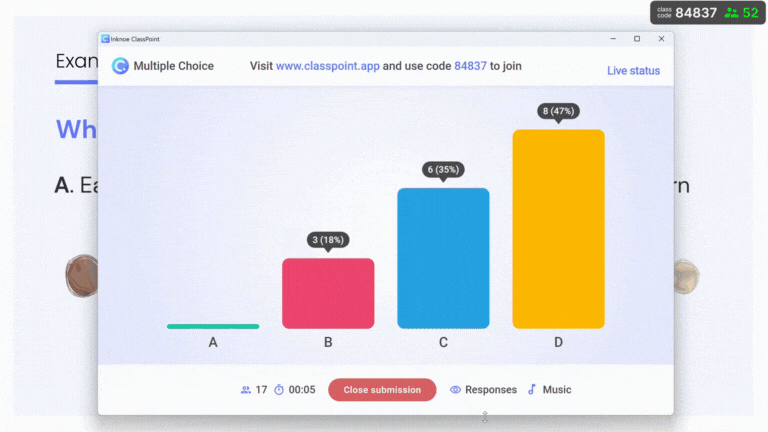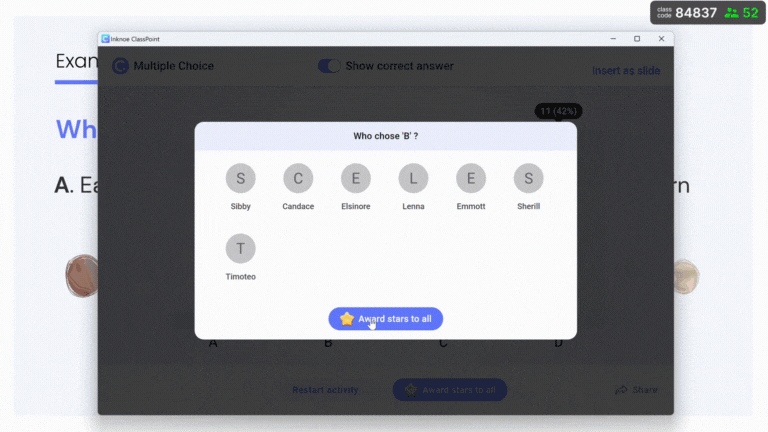
See a sample ClassPoint quiz in action 👇🏻
- Data-Driven Insights
Modern educational tools provide real-time analytics that help track student progress. Teachers can use this data to adjust instruction, offer targeted support, and develop strategies that cater to each student’s strengths and weaknesses.
ClassPoint's very own web app offers class session reports with individual student insights so you can better assess their performance and adjust instruction. The best part? Since this is web-based, access it anytime, anywhere.

2. Enhanced Educational Tools and Resources
- Interactive Learning Technologies
Modern technology tools, such as those powered by AI, facilitate engaging and hands-on learning experiences. These technologies make lessons more dynamic and encourage active participation, which can enhance cognitive skills.
From the very creators of ClassPoint, comes the next-gen AI for every educator. Edcafe is an advanced AI platform designed specifically for educators, offering tailor-fit teaching tools like interactive content creation, flashcards, slides generator, custom chatbots, and a dedicated resource hub to enhance teaching and learning experiences.

- Diverse Learning Materials
Access to a variety of multimedia resources—such as videos, interactive simulations, and online research—offers students different perspectives and problem-solving opportunities. This variety helps to keep students engaged and fosters critical thinking.
3. Emphasis on Early Childhood Education
- Foundational Skill Development
Early childhood education programs focus on essential skills like literacy, numeracy, and social-emotional development. These programs provide a strong foundation that supports long-term cognitive growth and academic success. - Parental Engagement
Increasing parental involvement in early education can reinforce learning at home and create a supportive environment. Strategies might include parent-teacher conferences, educational workshops, and at-home learning activities.
4. Promotion of Cognitive Stimulation
- Active Learning Strategies
Incorporating active learning techniques, such as group projects, hands-on experiments, and problem-based tasks, encourages deeper engagement with material. Active learning helps students develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Here's our quick guide on How to Create Engaging Lectures with Active Learning.
- Enrichment Opportunities
Providing extracurricular activities like coding clubs, science fairs, and art programs offers additional cognitive challenges. These activities extend learning beyond the classroom and stimulate intellectual curiosity.
We've covered proven effective activities to help facilitate better classroom management for all types of classrooms.
5. Focus on Mental and Physical Well-being
- Encouraging a Balanced Lifestyle
Promoting regular physical activity and outdoor play supports cognitive and physical health. Schools can integrate movement into daily routines and encourage activities that combine physical exercise with learning. - Supporting Mental Health
Addressing mental health needs and providing resources for stress management can improve cognitive performance. Schools might offer counseling services, stress-relief programs, and create a supportive environment for students’ emotional well-being.
Looking Ahead: Intelligence in the 21st Century
As we advance further into the 21st century, the concept of intelligence is evolving. While traditional IQ metrics have played a significant role in assessing cognitive abilities, there’s increasing recognition of non-IQ-based skills that are crucial for success in today’s world. Here’s a look at how these evolving definitions of intelligence might shape the future for Gen Alpha:

The Role of Non-IQ-Based Skills
- Emotional Intelligence (EQ)
Emotional intelligence involves the ability to understand and manage one’s own emotions, as well as the ability to empathize with others. In a world where collaboration and interpersonal skills are paramount, high EQ can lead to better leadership, teamwork, and conflict resolution. - Adaptability and Flexibility
The ability to adapt to changing circumstances and embrace new challenges is increasingly valued. As technology and job markets evolve, flexibility and the willingness to learn new skills will be essential for navigating career paths and personal growth. - Creativity and Innovation
Creativity is becoming a critical skill in a world that values problem-solving and innovation. Encouraging creative thinking and allowing students to explore new ideas can lead to groundbreaking solutions and advancements. - Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving
These skills involve analyzing information, making reasoned decisions, and solving complex problems. They are crucial for success in both academic and professional settings, where the ability to think critically and make informed decisions is highly valued.
Preparing for the Future
Educators and policymakers will need to adapt to these evolving definitions of intelligence by integrating skills development into curricula and fostering environments that support emotional and social growth. Emphasizing a balanced approach that values both traditional cognitive abilities and non-IQ-based skills will be key to preparing students for a dynamic future.
By acknowledging and nurturing these emerging aspects of intelligence, we can better equip Gen Alpha to thrive in an ever-changing world and redefine what it means to be truly intelligent in the 21st century.
