In today’s ever-evolving educational landscape, the concept of multisensory learning has been a head-turning pedagogy, often brow-raising even. As teachers navigate the complexities of diverse classrooms, they often face the challenge of addressing varied learning styles, engaging disinterested students, and ensuring meaningful comprehension.
Multisensory learning offers a promising solution, harnessing the power of multiple senses—sight, sound, touch, and movement—to create dynamic, interactive learning environments.
Yet, despite its potential benefits, many educators remain uncertain about how to effectively integrate multisensory techniques into their daily instruction. The traditional one-size-fits-all approach often falls short, leaving teachers searching for practical strategies to accommodate diverse needs and elevate learning outcomes. But, toss the worries out!
Together, we’ll explore the foundations, benefits, and actionable strategies of multisensory learning, empowering you to transform your classroom into a vibrant hub of multisensory exploration and discovery.
- Understanding the Foundations of Multisensory Learning
- The Neuroscience Behind Multisensory Learning
- Key Benefits of Multisensory Learning
- Practical Strategies for Implementing Multisensory Learning
- Implementing Multisensory Learning Strategies: Best Practices
- Food for Thought
Understanding the Foundations of Multisensory Learning
Historical Context and Evolution
Multisensory learning has roots that trace back centuries, evolving in response to changing educational philosophies and scientific understandings of human cognition. From ancient civilizations incorporating tactile and auditory methods to modern-day educators embracing a holistic approach, the evolution of multisensory learning reflects a continuous quest to optimize educational outcomes and cater to diverse learning needs.
Evolution of Multisensory Learning: A Timeline
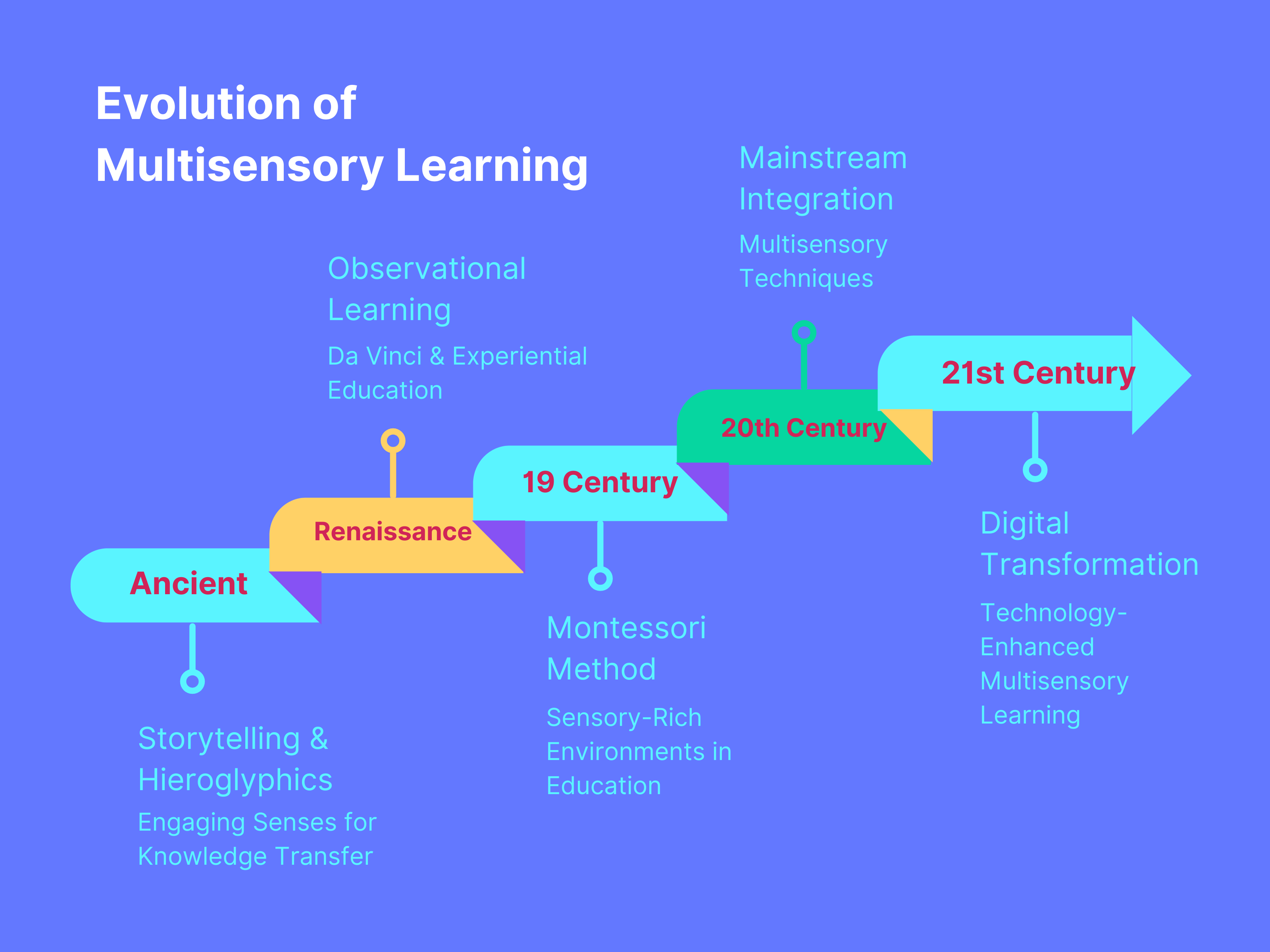
- Ancient Civilizations
- During ancient times, civilizations like the Greeks and Egyptians utilized a combination of storytelling, music, and hands-on activities to convey knowledge and wisdom. Philosophers such as Socrates engaged in dialogues, fostering critical thinking and oral tradition. Meanwhile, Egyptian hieroglyphics served as a multisensory medium, combining visual symbols with oral recitation and tactile inscriptions to preserve historical narratives and cultural practices.
- Renaissance Era
- The Renaissance period witnessed a resurgence of interest in experiential learning and sensory engagement. Visionaries like Leonardo da Vinci emphasized observational methods, encouraging students to explore the natural world through direct observation and hands-on experimentation. This era marked a shift towards holistic education, where creativity, curiosity, and multisensory experiences were valued as essential components of intellectual growth.
- 19th Century
- The 19th century heralded the introduction of systematic methods and pedagogical theories that supported multisensory instruction. Figures like Maria Montessori pioneered sensory-rich learning environments, emphasizing tactile materials, movement-based activities, and personalized learning experiences. Montessori’s innovative approach laid the groundwork for modern educational practices, highlighting the importance of engaging multiple senses to facilitate cognitive development and academic success.
- 20th Century
- The 20th century marked a pivotal era for multisensory learning, with significant advancements in psychology and neuroscience informing educational practices. Special education programs began integrating multisensory techniques to support students with diverse learning needs, recognizing the benefits of tailored approaches that catered to individual strengths and challenges. Mainstream classrooms also adopted multisensory strategies, incorporating visual aids, auditory cues, and kinesthetic activities to enhance engagement and comprehension across various subjects.
- 21st Century
- In the 21st century, the advent of technology revolutionized multisensory learning, leading to the development of digital platforms, interactive resources, and technology-enhanced tools. Educators leveraged virtual reality, augmented reality, and multimedia presentations to create immersive learning experiences that engaged multiple senses simultaneously. This digital transformation expanded the horizons of multisensory instruction, offering innovative solutions to address contemporary educational challenges and prepare students for a rapidly evolving global landscape.
Theoretical Frameworks Supporting Multisensory Approaches
Understanding the theoretical underpinnings of multisensory learning is crucial for effective implementation in the classroom. Below is a table outlining key theoretical frameworks, their core principles, and practical applications to guide educators in leveraging multisensory techniques effectively.
| Theoretical Framework | Key Principles | Practical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Constructivist Theory | Emphasizes active engagement and building upon prior knowledge to facilitate meaningful learning experiences. | Implement hands-on activities and project-based learning to encourage exploration and discovery. |
| Multiple Intelligences | Recognizes diverse strengths and learning styles, advocating for tailored instruction to meet individual needs. | Utilize varied assessments and differentiated instruction strategies to address students’ unique strengths and challenges. |
| Sensory Integration Theory | Focuses on integrating sensory inputs and facilitating neural connections to optimize cognitive development. | Incorporate tactile experiences and movement-based activities to engage multiple senses and enhance learning outcomes. |
| Cognitive Load Theory | Aims to manage information processing and optimize learning environments by minimizing cognitive overload. | Implement strategies such as chunking information and minimizing distractions to facilitate effective information processing and retention. |
| Experiential Learning Theory | Highlights the importance of direct experience and reflection in the learning process, emphasizing the role of concrete experiences, observations, and abstract conceptualization. | Foster experiential learning through real-world activities, reflective practices, and iterative feedback loops to promote deeper understanding and application of concepts. |
| Social Learning Theory | Explores how social interactions and observational learning influence cognitive development and behavior, emphasizing the role of modeling and collaborative learning experiences. | Encourage collaborative projects, peer interactions, and role-playing scenarios to facilitate social learning and interpersonal skills development among students. |
The Neuroscience Behind Multisensory Learning
Neural Pathways and Brain Engagement
Delving into the neuroscience of multisensory learning provides essential insights into its efficacy and influence on cognitive growth. As students utilize multiple senses, including sight, sound, touch, and movement, they stimulate diverse neural pathways. This stimulation enhances the processing and retention of information, contributing to a more comprehensive learning experience.
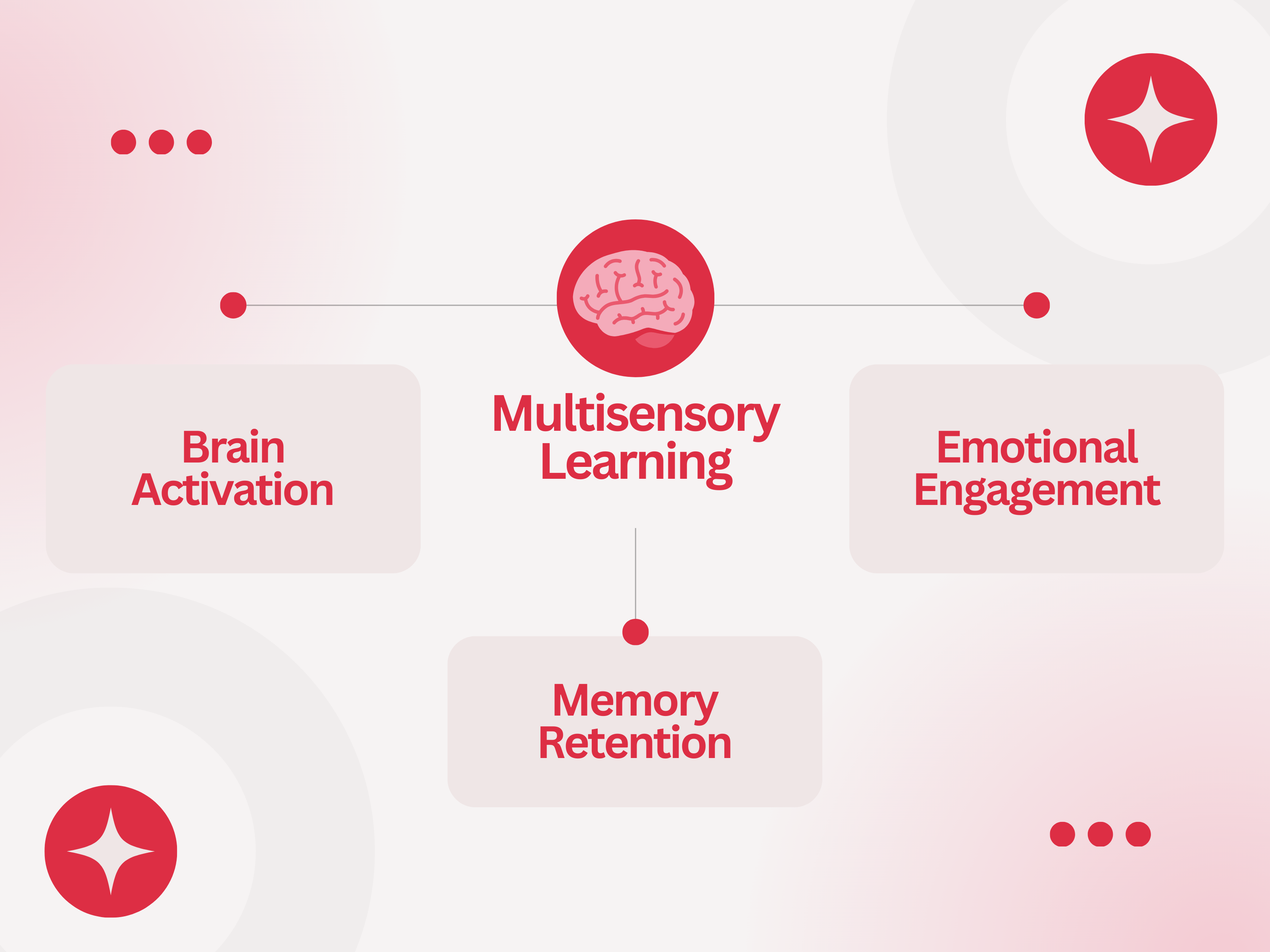
- Brain Activation: Multisensory activities stimulate different regions of the brain, promoting holistic cognitive development and fostering neural connections.
- Memory Retention: Engaging multiple senses facilitates deeper encoding of information, making it easier to retrieve and apply knowledge in diverse contexts.
- Emotional Engagement: Multisensory experiences often evoke emotional responses, enhancing motivation, and facilitating meaningful connections to content.
Research and Evidence Supporting Multisensory Approaches
Multisensory learning has garnered significant attention from educational researchers, leading to a plethora of studies that highlight its efficacy in enhancing student engagement, retention, and overall academic achievement. Below are some key findings supported by credible research:
- Improved Academic Performance
Numerous studies, such as the work by Pashler et al. (2008) in their review titled “Learning Styles: Concepts and Evidence“, suggest that multisensory approaches cater to diverse learning styles, leading to improved academic performance across various subjects and grade levels.
- Enhanced Memory Retention
According to a study by Dunn and Dunn (1992), titled “Teaching Secondary Students Through Their Individual Learning Styles“, multisensory learning strategies facilitate deeper encoding of information, thereby enhancing memory retention and recall abilities among students.
- Inclusivity and Equity
Research conducted by Fernald (2008) in “Enriching the Brain: How to Maximize Every Learner’s Potential” emphasizes that multisensory approaches promote inclusivity by accommodating diverse learning needs, thereby creating more equitable educational opportunities for all students.
- Engagement and Motivation
The research by Wolfe and Nevills (2004) in their book “Brain Matters: Translating Research into Classroom Practice” highlights that multisensory techniques increase student engagement and motivation by creating stimulating learning environments that cater to various sensory preferences.
- Neuroscientific Evidence
Neuroscientific studies, such as the research by Zull (2002) in “The Art of Changing the Brain,” provide empirical evidence supporting multisensory learning by demonstrating its impact on brain development, neural plasticity, and cognitive functioning.
Key Benefits of Multisensory Learning
Multisensory learning offers a myriad of benefits that enhance student engagement, memory retention, and overall academic achievement. By tapping into multiple senses, educators can create dynamic and inclusive learning environments that cater to diverse learning styles and needs. Here are some key benefits highlighted through emojis:
🧠 Enhanced Memory Retention
- Multisensory activities encourage students to process information through various sensory channels, facilitating deeper encoding and enhancing memory retention. This approach enables students to retrieve and apply knowledge more effectively in diverse contexts.
📚 Improved Academic Performance
- Multisensory learning caters to various learning styles, including visual, auditory, kinesthetic, and tactile, ensuring that students can access and process information in ways that resonate with their unique strengths and preferences.
🎯 Increased Student Engagement
- Multisensory activities create stimulating and interactive learning experiences that capture students’ attention, fostering active participation, curiosity, and intrinsic motivation to explore and learn.
🌍 Inclusivity and Accessibility
- Multisensory approaches accommodate diverse learning needs and styles, promoting inclusivity and accessibility by ensuring that all students have equitable opportunities to engage, participate, and succeed in the learning process.
🧩 Holistic Cognitive Development
- Multisensory learning stimulates various neural pathways, promoting holistic cognitive development, fostering neural connections, and enhancing critical thinking, problem-solving, and creative skills.
👥 Personalized Learning Experience
- Multisensory strategies allow educators to differentiate instruction and tailor learning experiences based on individual student strengths, preferences, and needs, creating personalized pathways to optimize learning outcomes.
😊 Emotional Engagement and Well-being
- Multisensory experiences evoke emotional responses, enhancing student motivation, satisfaction, and well-being by fostering positive attitudes towards learning, building confidence, and promoting a sense of accomplishment and fulfillment.
8 Practical Strategies for Implementing Multisensory Learning
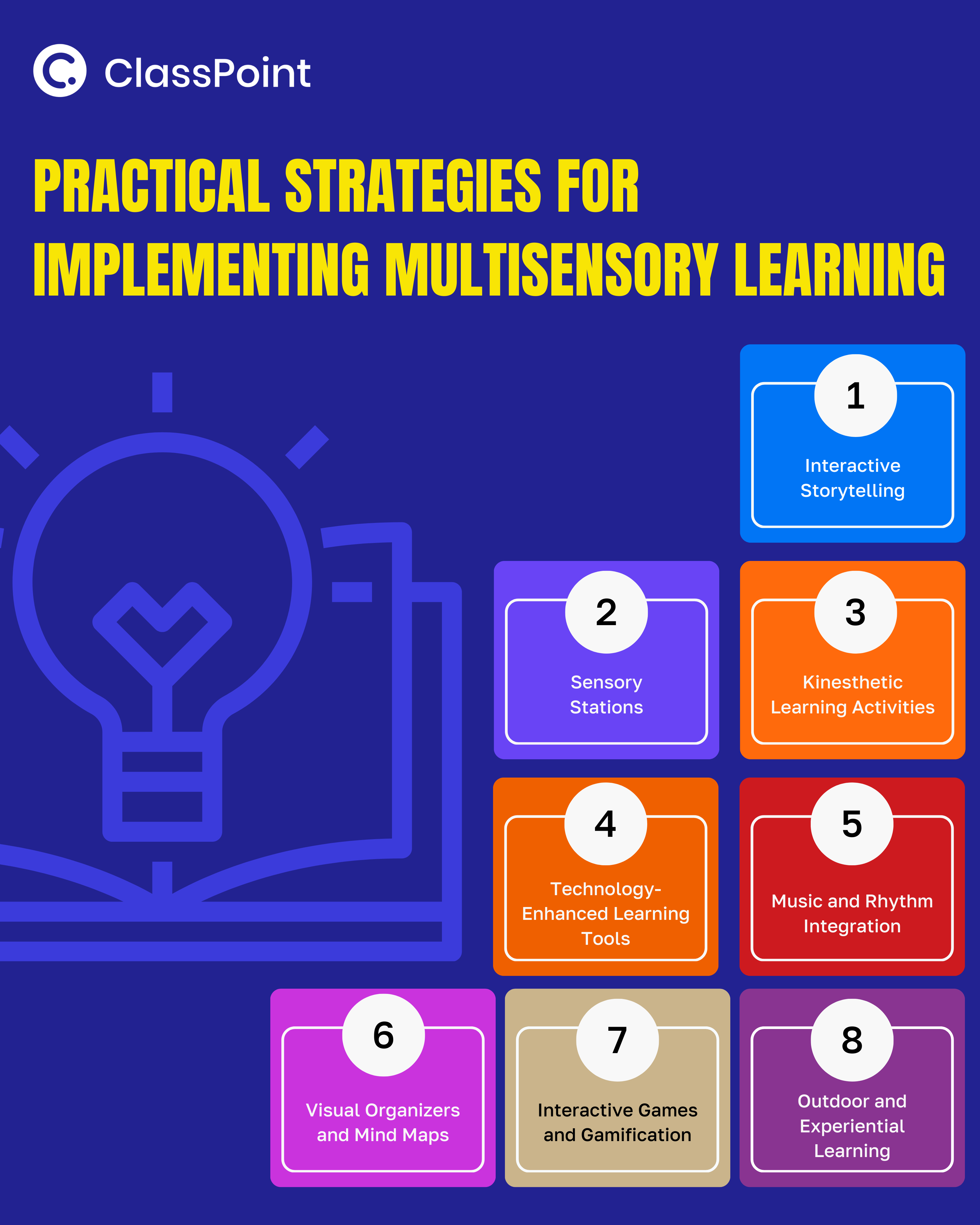
1. Interactive Storytelling
What it is: Interactive storytelling combines narrative elements with sensory-rich experiences to engage students in immersive learning journeys that promote comprehension, creativity, and critical thinking.
How to do it:
- Select a Theme: Choose a relevant topic or theme aligned with curriculum objectives.
- Incorporate Senses: Integrate visuals, sounds, props, and gestures to enhance storytelling and engage multiple senses.
- Engage Students: Encourage student participation through questioning, role-playing, and interactive activities that foster collaboration and deepen understanding.
Need some ideas on how to host interactive activities in the classroom? Check out a related story here.
2. Sensory Stations
What it is: Sensory stations are designated areas within the classroom where students can explore, manipulate, and interact with various materials and activities designed to stimulate different senses and facilitate experiential learning.
How to do it:
- Designate Areas: Create distinct stations or zones within the classroom, such as a tactile station with textured materials, an auditory station with sound-related activities, and a visual station with interactive visuals.
- Rotate Activities: Regularly rotate materials and activities to maintain student interest and cater to diverse sensory preferences.
- Monitor and Adapt: Observe student engagement and adapt stations based on feedback and evolving learning needs to optimize multisensory experiences.
3. Kinesthetic Learning Activities
What it is: Kinesthetic learning activities involve movement, physical manipulation, and hands-on exploration to facilitate experiential learning, enhance engagement, and promote motor skills development.
How to do it:
- Integrate Movement: Incorporate activities such as dancing, acting, and physical games that allow students to engage their bodies and minds simultaneously.
- Use Manipulatives: Provide hands-on materials and tools, such as puzzles, building blocks, and manipulatives, to facilitate tactile exploration and experiential learning.
- Connect to Content: Align kinesthetic activities with curriculum objectives and learning goals to ensure meaningful connections and reinforce key concepts.
4. Technology-Enhanced Learning Tools
What it is: Technology-enhanced learning tools, such as interactive classroom management apps, digital platforms, and virtual reality experiences, provide immersive and interactive learning opportunities that engage multiple senses and promote digital literacy skills.
How to do it:
- Select Appropriate Tools: Identify technology-enhanced learning tools that align with curriculum objectives, learning goals, and student needs.
- Integrate Seamlessly: Incorporate technology-enhanced activities into lesson plans, ensuring alignment with instructional goals and promoting active student engagement.
- Provide Guidance and Support: Offer guidance, support, and scaffolding to students as they navigate technology-enhanced learning experiences, fostering independence, confidence, and digital literacy skills.
Not quite sure which EdTech tool to go for? Make the choice with ClassPoint - the #1 audience engagement tool trusted by hundreds of thousands of teachers worldwide. ClassPoint redefines teaching in the classroom, giving you access to interactive quizzes, handy slide show tools, gamification features, and even an AI technology. The best part? It's all inside PowerPoint!
5. Music and Rhythm Integration
What it is: Incorporating music and rhythm into lessons can enhance engagement, facilitate memory retention, and stimulate various sensory experiences through auditory stimulation.
How to do it:
- Select Relevant Music: Choose music or rhythms that align with lesson themes or objectives.
- Integrate Activities: Incorporate singing, chanting, or rhythmic activities that reinforce content and engage students in auditory and kinesthetic learning experiences.
- Facilitate Reflection: Encourage students to reflect on how music and rhythm enhance their understanding and retention of key concepts.
Here're 3 innovative ways you can integrate music seamlessly in your PowerPoint presentations.
6. Visual Organizers and Mind Maps
What it is: Utilizing visual organizers and mind maps helps students organize information, make connections, and visualize complex concepts through spatial and visual processing.
How to do it:
- Create Visual Aids: Develop visual organizers, diagrams, or mind maps that represent key concepts, relationships, and processes.
- Facilitate Exploration: Encourage students to create their own visual organizers or mind maps to synthesize information, make connections, and demonstrate understanding.
- Promote Collaboration: Foster collaborative learning by incorporating group activities that involve creating, sharing, and discussing visual organizers or mind maps.
Check out these 5 best mind mapping tools for teachers.
7. Interactive Games and Gamification
What it is: Implementing interactive games and gamification strategies can enhance engagement, motivation, and learning outcomes by transforming traditional lessons into interactive and competitive experiences.
How to do it:
- Design Engaging Games: Develop interactive games, quizzes, or challenges that align with curriculum objectives and learning goals.
- Incorporate Rewards and Incentives: Integrate rewards, badges, or incentives to motivate students and promote active participation in gamified learning activities.
- Reflect and Adapt: Evaluate the effectiveness of gamification strategies, gather student feedback, and adapt games or incentives based on evolving learning needs and preferences.
Game face on! More on how you can gamify your PowerPoint presentations with ClassPoint here.
8. Outdoor and Experiential Learning
What it is: Outdoor and experiential learning opportunities provide hands-on experiences, environmental exploration, and sensory-rich activities that foster curiosity, creativity, and connection with nature.
How to do it:
- Plan Outdoor Activities: Design outdoor activities, field trips, or nature walks that align with curriculum objectives and promote experiential learning opportunities.
- Encourage Exploration: Facilitate student-led exploration, observation, and inquiry-based learning experiences in outdoor settings.
- Integrate Reflection: Incorporate reflective practices, discussions, or journaling activities to help students process their outdoor learning experiences and make connections to classroom content.
Implementing Multisensory Learning Strategies: Best Practices
Navigating the realm of multisensory learning requires a strategic approach that combines creativity, intentionality, and adaptability. As educators strive to create engaging and effective learning environments, implementing best practices becomes crucial. Below are some key guidelines distilled into actionable insights, each represented by a relevant emoji for easy reference and retention:
🎯 Align with Learning Objectives
Ensure that multisensory activities resonate with curriculum standards and set instructional goals, enhancing their relevance and impact.
🔄 Differentiate Instruction
Recognize and address individual student needs by customizing multisensory techniques to accommodate diverse learning styles and preferences.
📋 Provide Clear Instructions
Foster clarity and understanding by articulating instructions, expectations, and learning outcomes explicitly, setting students up for success.
🤝 Promote Active Engagement
Cultivate an environment of collaboration and interaction, encouraging students to engage deeply with multisensory techniques and each other.
📊 Incorporate Assessment and Feedback
Utilize formative assessments and timely feedback loops to gauge student progress and refine multisensory strategies effectively.
🔄 Reflect and Adapt Practices
Embrace a growth mindset by continuously evaluating and adapting multisensory approaches based on evolving student needs and instructional insights.
🤲 Collaborate and Share Resources
Harness the power of collaboration and professional development to share insights, resources, and strategies that amplify the impact of multisensory learning.
Food for Thought
As the educational landscape rapidly evolves, the incorporation of multisensory learning strategies emerges as a transformative catalyst, unlocking doors to engagement, comprehension, and innovation. From aligning with learning objectives to fostering collaboration and reflection, the journey towards multisensory mastery transcends traditional boundaries, ushering in a new era of dynamic and inclusive pedagogy.
As you embark on this transformative journey, remember that the essence of multisensory mastery lies not merely in technique but in the art of connection. Let us continue to innovate in shaping educational landscapes where every student finds their voice, discovers their passion, and embraces their potential.
