Project Based Learning (PBL) is transforming classrooms by immersing students in real-world challenges and fostering a deeper understanding through hands-on experiences. If you’re seeking innovative Project Based Learning Ideas, you’re in the right place.
We aim to fill in gap in traditional education resource and guides, by providing you with practical examples of effective project-based learning initiatives across different education levels.
Keep reading to discover how to bring Project Based Learning to life in your classroom:
Understanding Project-Based Learning (PBL)
What is Project Based Learning?
Project-Based Learning (PBL) is an educational approach that goes beyond textbooks and tests. It’s where students actively explore real-world problems and challenges, gaining knowledge and skills through hands-on projects. Project Based Learning is not just a teaching method; it’s a journey into the heart of learning, fostering critical thinking, creativity, and collaborative skills.
Key Principles of Project-Based Learning

Project-Based Learning (PBL) is built on a set of core principles that distinguish it from traditional educational methods. These principles are the bedrock of creating a dynamic and effective Project Based Learning environment:
- Student-Centered Learning: Project-Based Learning puts students at the heart of the learning process. They take the lead in their projects, making decisions, solving problems, and directing their learning paths. This autonomy builds confidence and a sense of ownership over their work.
- Inquiry and Exploration: At the core of Project Based Learning is the spirit of inquiry. Students are encouraged to ask questions, seek out new information, and explore different perspectives. This approach fosters a deeper understanding and a more meaningful connection with the subject matter.
- Real-World Relevance: Project Based Learning projects are often tied to real-world scenarios, making learning more relevant and engaging for students. By tackling issues that matter in the real world, students see the practical application of their studies and are more motivated to learn.
- Collaboration: Project Based Learning often involves group work, where students collaborate, share ideas, and learn from each other. This collaborative environment helps develop communication and teamwork skills, which are vital in both academic and professional settings.
- Reflection and Revision: An integral part of Project Based Learning is reflecting on what’s been learned and how it’s been learned. Students are encouraged to think critically about their work and make revisions, learning that iteration is a key part of the creative process.
- Presentation and Sharing: Sharing their work with others is a common end-goal in Project Based Learning. This aspect helps students develop presentation skills and also allows for feedback from peers and teachers, which is crucial for learning and improvement.
How PBL Differs from Traditional Education
| Aspect | Traditional Education | Project-Based Learning (PBL) |
|---|---|---|
| Role of the Teacher | Primarily a source of information, leading the classroom with lectures. | Acts as a facilitator or guide, fostering a collaborative learning environment. |
| Learning Environment | Structured around lectures and individual work. | Emphasizes collaboration, hands-on activities, and a dynamic, engaging atmosphere. |
| Assessment Methods | Relies on standardized tests and quizzes. | Assesses students based on projects, presentations, and the learning process itself, offering a holistic view of skills and understanding. |
| Learning Outcomes | Focuses on memorizing facts and theories. | Stresses the application of knowledge, problem-solving, and critical thinking, equipping students for real-world scenarios. |
Why Project-Based Learning Works

Project-Based Learning stands out as a transformative educational approach, aligning perfectly with modern pedagogical needs and theories. Its effectiveness and popularity in educational settings stem from its ability to engage students, develop essential life skills, and cater to diverse learning styles, all while preparing them for real-life challenges. Here’s an integrated look at why project-based learning works so well, also linking it to key educational theories and practices:
- Engagement and Motivation: The hands-on approach of project-based learning makes learning more engaging and enjoyable. This increased interest leads to higher motivation and information retention. It aligns with Social and Emotional Learning (SEL), where emotional engagement is crucial for educational success.
- Develops Critical Skills: Critical thinking, problem-solving, collaboration, and communication are at the heart of project-based learning, echoing principles from constructivism. These skills are essential for navigating the complexities of the 21st-century world.
- Adapts to Diverse Learning Styles: The adaptability of project-based learning to various learning styles—visual, auditory, kinesthetic—makes it a highly inclusive educational approach. This flexibility reflects principles of cognitive learning theory, which emphasizes catering to individual cognitive processes.
- Encourages Lifelong Learning: By fostering curiosity and a love for learning, project-based learning helps cultivate lifelong learners, an aspect crucial in today’s fast-evolving world. This trait is a cornerstone of inquiry-based learning, which encourages perpetual curiosity and questioning.
- Real-World Application: Project-based learning prepares students for real-life scenarios, linking academic learning to real-world applications. This approach enhances students’ ability to apply classroom learning in external situations, a key aspect of preparing them for future challenges.
- Customizable and Flexible: The ability to tailor project-based learning to any subject matter and age group makes it an effective strategy across educational contexts. Its flexibility allows educators to mold it according to their classroom dynamics and student needs.
- Feedback and Improvement: Project-based learning involves an iterative process where students create, receive feedback, and improve. This reflects real-world problem-solving and continuous improvement processes, essential for student development.
A Closer Look of Project-Based Learning Across Educational Levels
Project-Based Learning (PBL) isn’t a one-size-fits-all approach; it’s versatile, catering to a wide range of learners. Understanding the target audience for Project Based Learning ideas is key to tailoring projects that resonate and inspire. Here’s a closer look:
- Kindergarten kids
- Elementary school students
- Middle schoolers
- Educators and teachers
- High school students
- Higher education students
- Parents
Project Based Learning is a dynamic educational approach that adapts to the needs and abilities of different age groups, making it an effective tool for inclusive and comprehensive learning. By tailoring PBL ideas to the specific audience, educators can ensure that learning is not only effective but also enjoyable.
Project-Based Learning in Kindergarten

Project-Based Learning (PBL) in kindergarten is a magical journey of discovery and creativity. At this foundational stage, Project Based Learning is not just about learning facts; it’s about sparking curiosity, fostering creativity, and developing social skills. Here’s how Project Based Learning unfolds in a kindergarten setting:
Embracing Exploration and Discovery
- Sensory-rich Projects: Young children learn best through sensory experiences. Project Based Learning in kindergarten often involves activities that engage the senses – touch, sight, sound, and even taste. Projects like creating a sensory garden or a tactile art piece allow children to explore and learn through direct interaction with materials.
- Story-based Learning: Stories captivate children’s imaginations like nothing else. Integrating storytelling into Project Based Learning can make learning more engaging. For instance, after reading a story about animals, children could engage in a project to create their own animal habitat.
Fostering Creativity and Expression
- Art and Craft Projects: These projects are a staple in kindergarten Project Based Learning. Children could create a mural depicting seasons, craft their own musical instruments, or build models using recyclable materials. Such activities not only unleash creativity but also enhance fine motor skills.
- Role-playing and Dramatization: Children love to pretend and role-play. Projects that involve dramatization, like reenacting a folk tale or creating a mini-theater show, help develop language skills and confidence.
Building Social and Emotional Skills
- Collaborative Projects: Group activities where children work together to achieve a common goal are excellent for teaching teamwork and empathy. Building a classroom treehouse model or a community helpers’ chart are projects that encourage collaboration.
- Emotional Learning Projects: Activities that focus on recognizing and expressing emotions, like creating an ‘emotions chart’ or storytelling sessions where children discuss feelings, are valuable for emotional development.
Use ClassPoint's Name Picker to randomly select and group students during collaborative projects.
Integrating Basic Academic Concepts
- Mathematics Through Play: Projects like setting up a pretend shop can teach basic counting and arithmetic in a fun way. Children learn best when they don’t even realize they’re learning!
- Environmental Awareness: Projects that involve observing and interacting with nature, like planting a garden or observing weather changes, introduce science concepts in a tangible and enjoyable manner.
Involving Parents and Community
- Family Collaboration Projects: Involving parents in projects, like creating a family tree or a ‘my neighborhood’ map, not only enhances learning but also strengthens the home-school connection.
- Community Engagement: Projects that connect children with their community, like visiting a local fire station or creating artwork for a community center, help them understand their role in the larger world.
Project-Based Learning in Elementary School

Project-Based Learning (PBL) in elementary school lays the groundwork for a lifetime of curious, engaged learning. It’s here that children first encounter the joys of discovery and the satisfaction of solving problems. Let’s explore how Project Based Learning can be effectively implemented at this crucial stage of education through various collaborative projects.
Environmental Awareness Projects
- Building a Mini Ecosystem: Students create a small-scale ecosystem, learning about biology, sustainability, and environmental science.
- Designing a Sustainable Garden: Pupils plan and cultivate a garden, learning about plant life, sustainable practices, and teamwork.
Historical Exploration Projects
- Creating a Historical Timeline: This project involves researching and illustrating significant historical events, enhancing understanding of history and the concept of time.
- Cultural Exploration Project: Students explore and present different cultures, fostering global awareness and appreciation for diversity.
Try using ClassPoint's Draggable Objects for interactive timeline teaching.
Scientific Inquiry Projects
- Young Meteorologist Program: Students explore weather patterns, conduct simple experiments, and present their findings on local weather phenomena.
- Simple Machines Playground: A project where students learn about basic physics by designing and building simple machines.
Art and Creativity Projects
- Community Mural Creation: A group project focused on creating a mural that represents the local community or a theme studied in class.
- Storybook Creation: Students write and illustrate their own storybooks, blending creative writing with artistic expression.
Mathematics and Problem-Solving Projects
- Math in Real Life: A project where students apply mathematical concepts to solve real-world problems, like budgeting for a mini event.
- Geometry in Architecture: Pupils use geometric shapes to design simple structures, understanding geometry’s practical applications.
Pro Tip: Use ClassPoint's Slide Drawing to invite students to submit their responses for math problems. Check out these 5 slide drawing activities you can easily implement in your classroom.
Pro Tip: Make projects as relevant to the real world as possible. For instance, a gardening project can be tied to lessons on healthy eating or environmental conservation. Have regular check-ins and reflections on the project using ClassPoint's interactive quizzes. And encourage parents to get involved in projects, either by providing resources or by participating in certain activities.
Project-Based Learning in Middle School

Middle school is a pivotal time in students’ educational journeys, making it an ideal stage for implementing Project-Based Learning (PBL). This period is characterized by students’ growing abilities to think abstractly, reason logically, and engage with more complex subject matter. Project Based Learning in middle school harnesses these developmental strides, turning the classroom into a dynamic learning environment.
The Role of Project Based Learning in Middle School Education
- Fostering Independence: Middle school students are at an age where they crave independence. Project Based Learning offers them the chance to take charge of their learning, making choices and solving problems with minimal hand-holding.
- Catering to Varied Interests: At this age, students are exploring their interests. Project Based Learning can be tailored to these diverse interests, making learning more relevant and engaging.
- Building Critical Thinking: Middle schoolers are developing critical thinking skills. Project Based Learning challenges them to analyze, evaluate, and create, pushing their cognitive abilities.
Engaging Middle School Students with Project Based Learning
To engage middle school students effectively, Project Based Learning should be:
- Relevant and Real-World Focused: Projects should tie into real-world problems or students’ interests to keep them engaged and invested.
- Collaborative: Group projects encourage social interaction and teamwork, skills that are crucial during these formative years.
- Varied in Complexity: Projects should vary in complexity to cater to different learning levels and to keep all students challenged and interested.
- Ask Open-Ended Questions: Encourage students to ask and answer ‘why’ and ‘how’ questions, pushing them to think more deeply about their projects.
- Encourage Problem-Solving: Present students with real problems to solve in their projects, requiring them to think critically and creatively.
- Foster Debate and Discussion: Create opportunities for students to discuss and debate different aspects of their projects, encouraging them to consider various viewpoints and defend their ideas.
Refer to this bloom's taxonomy questions dictionary for inspiration of higher-order thinking questions to ask.
Examples of Project-Based Learning Ideas for Middle School
- Simulating Historical Events: Students could recreate a significant historical event, which helps them understand the complexities of history and its impact on the present.
- Designing and Building a Model City: This project incorporates principles of urban planning, environmental science, and engineering, encouraging students to think about sustainability and community planning.
- Investigating Environmental Issues: Students could explore current environmental challenges, conduct research, and propose actionable solutions. This project can also include a community service aspect, like a neighborhood clean-up or awareness campaign.
Assessing Middle School Project-Based Learning Projects
Assessment in Project Based Learning should be as dynamic as the learning process:
- Rubrics: Use detailed rubrics that assess various aspects of the project, from the research and planning stages to the final presentation.
- Peer and Self-Assessment: Encourage students to give and receive feedback. This process helps them develop critical thinking and reflective skills.
- Teacher Evaluation: Teacher assessment should focus not only on the end product but also on the learning process, including how students worked together, solved problems, and overcame challenges.
Conduct quick and seamless live assessments and quizzes within PowerPoint using ClassPoint's interactive quiz buttons.
Project-Based Learning in High School

High school students are on the brink of entering higher education or the workforce. At this pivotal stage, project-based learning (PBL) can be a powerful tool to prepare them for the future.
Civic Engagement Projects
- Local History Documentation: Students research and document the history of their community, culminating in a presentation or a digital archive.
- Public Policy Analysis: Analyze a current policy issue, develop alternative solutions, and present findings to local stakeholders.
STEM Innovation Projects
- Robotics Challenge: Design and build a robot to perform specific tasks, integrating principles of engineering and computer science.
- Sustainable Energy Solutions: Research and propose alternative energy solutions for the school, presenting a feasible plan to the administration.
Creative Arts and Expression Projects
- Theatre Production: Produce and perform a play, allowing students to explore literature, history, and the performing arts.
- Art Installation: Create an art installation that comments on a social issue, combining art with social studies.
Pro Tip: Guide students to critically analyze their findings and consider the implications of their projects on society. Craft questions that promote critical analysis using ClassPoint AI. We also recommend teachers to encourage projects that require knowledge from multiple disciplines to solve complex problems, reflecting real-world scenarios.
Project-Based Learning in Higher Education

In higher education, PBL is an excellent way to bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application.
Research and Development Projects
- Undergraduate Research Project: Conduct original research in a chosen field of study, with the goal of presenting findings at a conference or publishing.
- Startup Incubator: Develop a business plan and prototype for a startup idea, potentially collaborating with business and engineering departments.
Community and Global Impact Projects
- Community Service Initiative: Design and implement a service project that addresses a local need, reflecting on the social impact.
- Global Collaboration Project: Collaborate with students from a university abroad to address global challenges, promoting cross-cultural understanding and cooperation.
Tips for Effective PBL at the Collegiate Level
- Encourage Scholarly Research: Promote the use of scholarly databases and research methods to deepen academic rigor in projects.
- Collaborate Across Departments: Take advantage of the diverse academic departments to build interdisciplinary projects that mirror professional and research complexities.
- Incorporate Industry Tools: Use industry-standard tools and methodologies to give students hands-on experience with the tools they will encounter in their careers.
- Global Perspective: Encourage projects that require students to engage with global issues or collaborate with international peers, expanding their cultural competence and global awareness.
- Outcome-Oriented Projects: Design projects with tangible outcomes, like published research, implemented programs, or exhibited works, to add to students’ portfolios and resumes.
Combine PBL with formative assessments using ClassPoint Quiz Mode with automatic grading. Here are 30 formative assessment questions to ask your students.
8 Project-Based Learning Strategies You Cannot Miss!

Implementing Project-Based Learning (PBL) can be a game-changer in education, but it requires a thoughtful approach to ensure success. Here’s how educators can effectively integrate Project Based Learning into their teaching:
- Start with Clear Goals: Define what you want to achieve with Project Based Learning. Are you focusing on developing specific skills, enhancing knowledge in a subject area, or fostering collaboration? Clear goals help in designing more focused and effective projects.
- Design Engaging Projects: The heart of Project Based Learning is the project itself. Design projects that are challenging yet achievable, relevant to students’ interests and real-world problems. Ensure they align with educational standards and learning objectives.
- Facilitate, Don’t Dictate: Shift from a teacher-led to a student-centered approach. Guide students through the process, but give them autonomy to make decisions and solve problems. This fosters independence and critical thinking.
- Incorporate Technology Wisely: Utilize technology to enhance Project Based Learning. Tools like ClassPoint can be used to create interactive presentations, conduct real-time quizzes, and provide instant feedback, making the learning process more dynamic and engaging.
- Build a Collaborative Environment: Encourage teamwork and collaboration among students. Group projects can help develop communication skills and the ability to work effectively with others.
- Continuously Assess and Reflect: Assessment in Project Based Learning goes beyond traditional tests. Include formative assessments throughout the project, encourage self and peer assessments, and have students reflect on their learning process and outcomes.
- Be Prepared for Challenges: Implementing Project Based Learning can come with challenges like managing diverse learning styles, ensuring equal participation, and aligning projects with curriculum standards. Be proactive in addressing these challenges and be flexible in your approach.
- Seek Feedback and Evolve: After each project, seek feedback from students and colleagues. Use this feedback to refine your approach and evolve your Project Based Learning strategies over time.
Successful implementation of Project Based Learning doesn’t happen overnight. It’s a journey that involves continuous learning, adaptation, and a commitment to creating engaging and meaningful learning experiences for students. By following these strategies, educators can effectively integrate Project Based Learning into their classrooms, making learning more interactive, enjoyable, and impactful.
Bonus: Getting Started with Project-Based Learning Using ClassPoint
ClassPoint is not just an add-on for PowerPoint; it’s a powerful tool that can transform your approach to Project-Based Learning (PBL). Here is a step-by-step guide on how you can use ClassPoint to bring your PBL ideas to life.
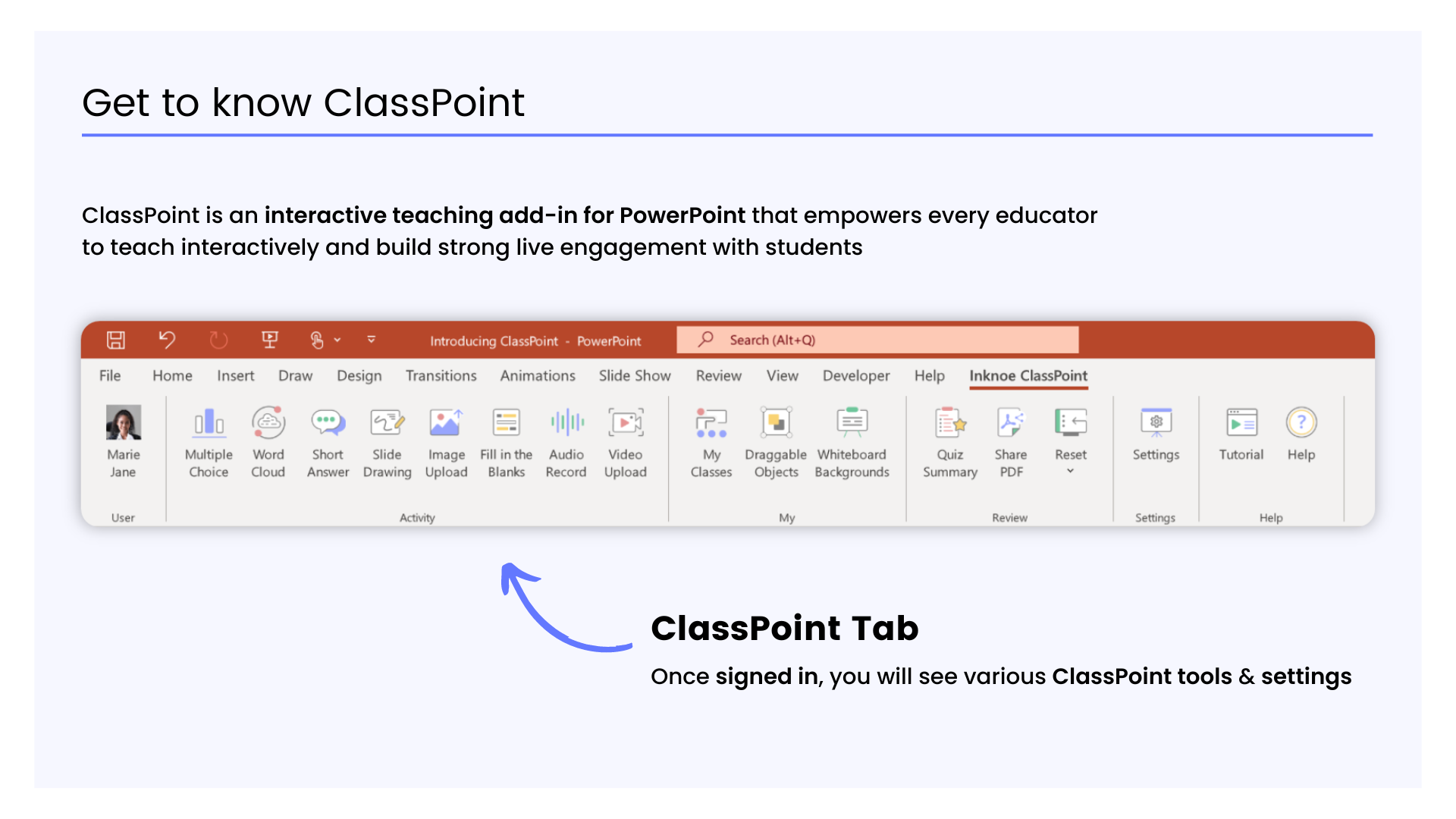
Step-by-Step Implementation:
- Concept Introduction: Use ClassPoint’s Quick Poll or Word Cloud feature to survey students on their initial thoughts about a new topic.
- Project Proposal: Students articulate their project ideas in a short, written format and submit these proposals to the teacher for approval using Short Answer.
- Research and Design: Students conduct research using traditional methods or their devices and compile their findings in PowerPoint. The teacher can also facilitate this step by using ClassPoint’s embedded browser to showcase websites or resources during the presentation for guidance.
- Student Presentation: Students present their completed projects, integrating multimedia elements such as videos and images, alongside live demonstrations to showcase their work effectively.
- Audience Engagement: Encourage students to leverage ClassPoint’s draggable objects, live quizzes or quick polls to interact with other students and allow the audience to vote on their favorite projects or to facilitate a question-and-answer session.
- Assessment & Feedback: Implement real-time polling for a quick knowledge check and collect feedback from classmates, making the session interactive and engaging.
Check out these 8 Drag and Drop activities, and 50 interactive quiz ideas to drive classroom engagement.
Take the Next Step in Project-Based Learning
You’ve seen the power of project based learning ideas – now it’s time to bring them into your classroom. With ClassPoint’s interactive features, you can elevate these projects from concept to reality.
- Turn your PowerPoint into an interactive learning hub.
- Engage students with real-time quizzes and polls.
- Track progress and celebrate achievements with gamification.
Don’t just read about it – experience the transformation. Try ClassPoint for free and watch your project based learning ideas come to life!

