In the ever-evolving landscape of education, understanding the dynamics of how students learn is crucial. One of the most influential theories that educators can leverage to enhance learning experiences is social learning theory. This theory has profound implications for classroom dynamics, teaching strategies, and student engagement.
Whether you are a seasoned educator, a student aspiring to understand learning mechanisms better, or a professional in the field of education, grasping the fundamentals of social learning theory can significantly impact how you approach teaching and learning.
This comprehensive guide delves into the basics, core concepts, key factors, and practical applications of social learning theory, offering valuable insights and actionable strategies for educational success.
What is Social Learning Theory?
Social learning theory, developed by psychologist Albert Bandura, is a framework for understanding how individuals acquire new behaviors, skills, and attitudes through observation and imitation of others. Unlike traditional learning theories that emphasize direct reinforcement and punishment, social learning theory highlights the importance of social context and the interactions between individuals.
At its core, social learning theory posits that people can learn by watching others, a process known as observational learning. This theory integrates cognitive, behavioral, and environmental influences, suggesting that learning is a complex interplay between these factors. It recognizes that while direct experiences are essential, much of what we learn comes from observing the actions and outcomes of others’ behaviors.
Key Components of Social Learning Theory

- Observational Learning: Learning by observing the behavior of others and the consequences of those behaviors.
- Imitation and Modeling: The process of replicating behaviors observed in others, which can include attitudes, emotional reactions, and skills.
- Attention, Retention, Reproduction, and Motivation: Four key processes that influence observational learning:
- Attention: The learner must pay attention to the model and the behavior being demonstrated.
- Retention: The learner must be able to remember the behavior that has been observed.
- Reproduction: The learner must be capable of reproducing or imitating the observed behavior.
- Motivation: The learner must have the desire or motivation to perform the behavior.
Social learning theory also underscores the role of reinforcement and punishment, not just through direct experiences but also by observing the consequences of others’ actions. This vicarious reinforcement or punishment can significantly influence whether a behavior is adopted or discarded.
The Origins and Evolution of Social Learning Theory
Social learning theory was introduced by Albert Bandura in the 1960s. Bandura’s work was groundbreaking, as it integrated behavioral and cognitive perspectives on learning.
Key Experiment: The Bobo Doll Experiment
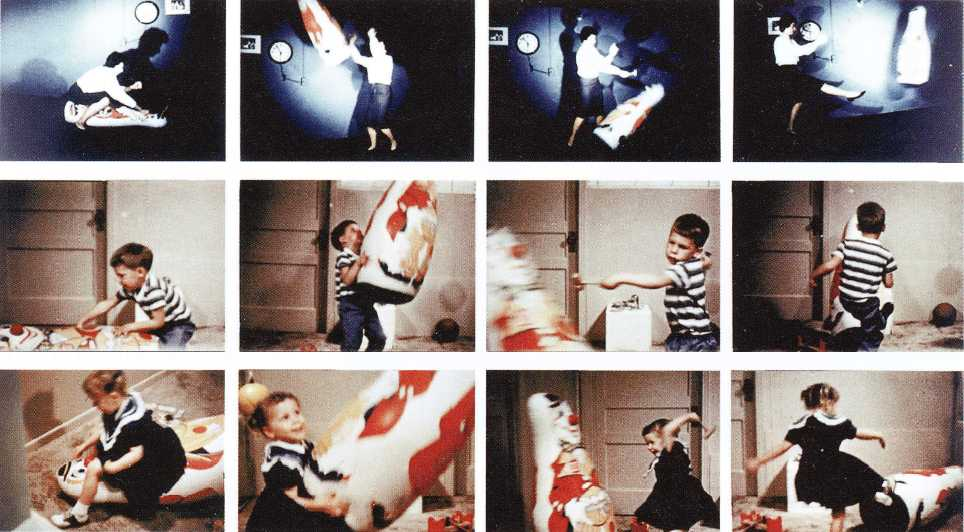

One of the most iconic studies illustrating social learning theory is Bandura’s Bobo doll experiment. In this study, children observed adults behaving aggressively towards a Bobo doll—a large inflatable toy that bounces back when hit. The adults kicked, punched, and verbally attacked the doll while the children watched.
When these children were later given the opportunity to play in a room with a Bobo doll, many of them imitated the aggressive behaviors they had observed. Despite not receiving any direct reinforcement or encouragement for these actions, the children replicated both the physical and verbal aggression demonstrated by the adults. This experiment vividly demonstrated that learning could occur through observation alone, highlighting the power of modeled behavior.
Progress in Social Learning Theory
Following the Bobo doll experiment, social learning theory continued to develop, incorporating a broader range of cognitive and environmental factors. Bandura recognized that learning is not merely a behavioral change but also involves cognitive processes. This shift led to a more comprehensive understanding of how individuals acquire new behaviors and information through observation.
The theory expanded to consider the importance of self-efficacy—an individual’s belief in their own ability to succeed in specific situations. Bandura’s later work emphasized how self-efficacy influences learning and behavior, suggesting that people are more likely to adopt behaviors they believe they can successfully execute.
What’s Next for Social Learning Theory
Today, social learning theory is applied across various fields, including education, psychology, sociology, and media studies. It provides a robust framework for understanding how people learn from their social environment and the influence of modeled behavior.
In education, the principles of social learning theory are used to create more interactive and engaging learning experiences. Teachers incorporate modeling, peer learning, and collaborative activities to enhance student engagement and retention.
Looking forward, the integration of technology in education offers new opportunities for applying social learning theory. Digital platforms and social media provide rich environments for observational learning, allowing students to observe and interact with diverse role models and peers globally.
Impact on Education
By recognizing the power of social interactions and environmental influences, social learning theory offers valuable insights that can enhance educational practices and foster more effective learning experiences. Understanding and leveraging these principles can help educators create more dynamic and responsive learning environments that cater to the diverse needs of students.
Social learning theory continues to evolve, integrating new research and technological advancements to better understand and facilitate human learning in an increasingly interconnected world.
Benefits of Social Learning Theory in Education
Implementing social learning theory in educational settings offers numerous benefits across various dimensions of student development. The table below summarizes these benefits:
| Aspect | Benefits | Context |
|---|---|---|
| Student Engagement | Increased Participation | Social learning strategies such as group work and role-playing encourage active participation and involvement in the learning process. |
| Academic Performance | Improved Test Scores | Techniques like peer tutoring and cooperative learning have been shown to enhance understanding and retention, leading to higher test scores. |
| Social Skills | Enhanced Communication and Collaboration | Activities that require teamwork and peer interaction help students develop essential social skills such as communication, collaboration, and empathy. |
| Self-Efficacy | Greater Confidence and Motivation | Observing peers and receiving positive reinforcement boosts students’ confidence in their abilities and motivates them to take on new challenges. |
| Critical Thinking | Development of Analytical and Problem-Solving Skills | Engaging in discussions, peer review, and collaborative problem-solving activities fosters critical thinking and analytical skills. |
| Behavioral Outcomes | Positive Behavioral Changes | Modeling and observing positive behaviors in the classroom lead to improved student conduct and reduced behavioral issues. |
| Retention of Material | Better Long-Term Retention | Social learning activities such as collaborative projects and gamified learning help students retain information longer by making learning more interactive and memorable. |
| Adaptability | Enhanced Ability to Adapt to New Situations | Exposure to diverse perspectives and problem-solving approaches through social learning prepares students to adapt to various situations and challenges. |
| Inclusivity | Greater Inclusivity and Peer Support | Social learning creates a supportive environment where all students, regardless of their abilities, feel included and valued. |
10 Use Cases of Applying Social Learning Theory in the Classroom
1. Peer Tutoring Programs
Peer tutoring involves students teaching and assisting their classmates, which helps both the tutor and the tutee. Tutors reinforce their understanding of the subject by explaining it, while tutees benefit from peer explanations, which can be more relatable than teacher-led instruction.
How you can do it: Organize peer tutoring sessions by pairing high-achieving students with those who need extra help. Create a structured schedule and provide training and resources for the tutors to ensure they are effective in their roles.
How it helps: This approach enhances comprehension for both tutors and tutees. Tutors reinforce their own knowledge and develop teaching skills, while tutees receive personalized assistance and benefit from peer support, fostering a collaborative learning environment.
2. Cooperative Learning Groups
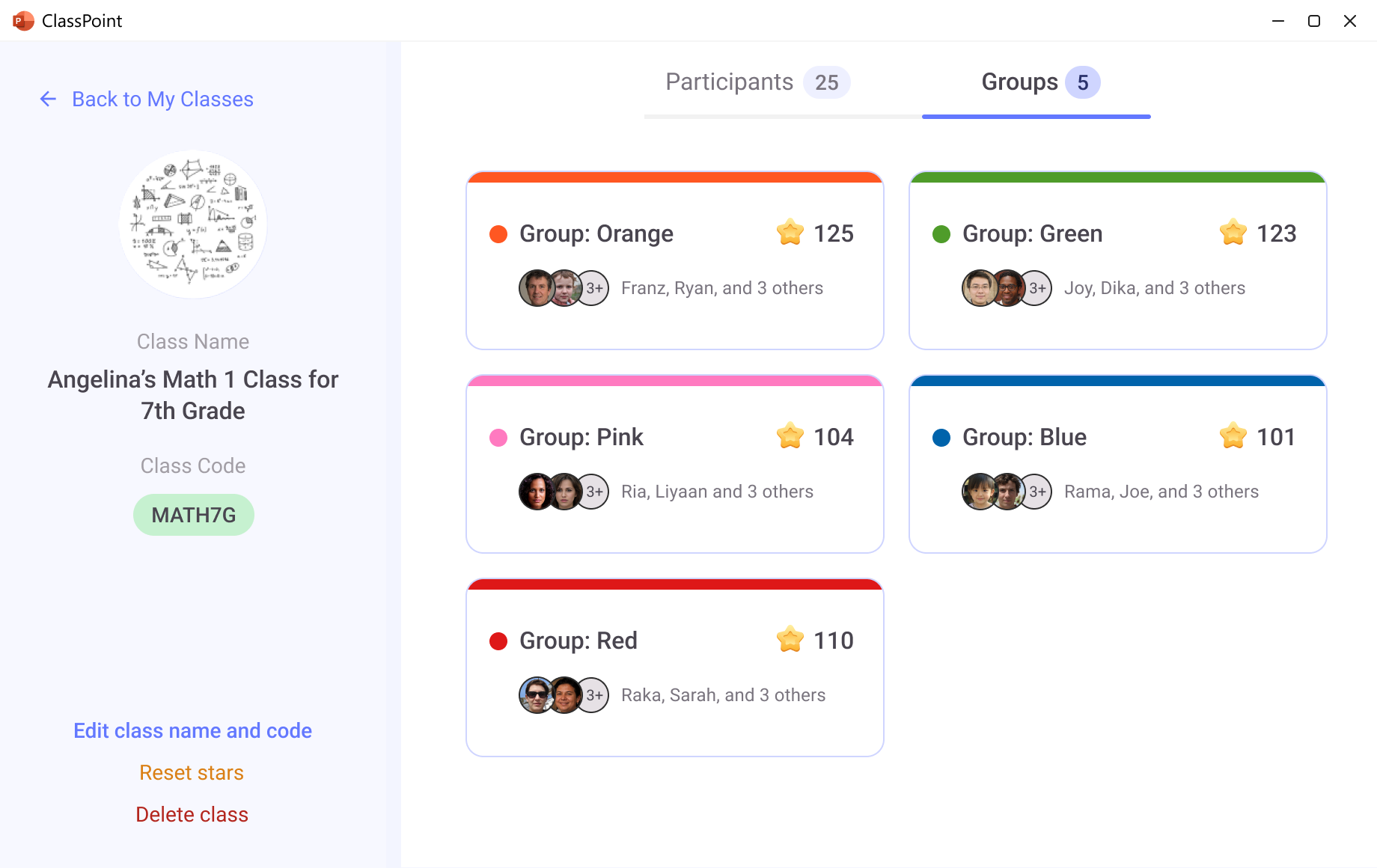
Cooperative learning groups involve students working together in small groups to complete tasks, solve problems, or conduct experiments. This method encourages interaction, discussion, and shared responsibility among students.
How you can do it: Assign group projects or tasks that require collective problem-solving and research. Rotate group members to ensure diverse interactions and experiences. Provide clear instructions and roles to ensure each student participates actively.
ClassPoint's grouping feature is the perfect fit to make forming groups among students easier by letting you do it in the familiar interface of PowerPoint.
How it helps: Cooperative learning fosters communication, teamwork, and critical thinking. Students learn from each other by observing different approaches and strategies, enhancing their understanding and retention of the subject matter.
3. Classroom Role-Playing
Role-playing allows students to act out scenarios related to the lesson, helping them understand different perspectives and practice social behaviors in a controlled environment.
Read more on our take about Behavioral Learning Theory here.
How you can do it: Design role-playing activities relevant to the lesson content. Assign roles to students and provide them with a context or scenario to act out. Encourage them to reflect on the experience and discuss their observations afterward.
How it helps: Role-playing promotes empathy, communication, and problem-solving skills. It enables students to explore and understand different viewpoints, making abstract concepts more tangible and memorable.
Use ClassPoint's name picker to match students and their roles randomly to encourage diversity.
4. Interactive Demonstrations
Interactive demonstrations involve teachers performing live demonstrations of experiments, problem-solving methods, or practical skills, allowing students to observe and then practice the behaviors themselves.
How you can do it: Regularly demonstrate key concepts and skills in class, using step-by-step instructions and visual aids. Encourage students to participate and ask questions during the demonstration, and provide opportunities for them to practice what they’ve observed.
How it helps: Demonstrations provide a clear model for students to follow, making it easier for them to understand and replicate complex processes. This hands-on approach enhances engagement and retention by involving multiple senses in the learning process.
5. Use of Educational Videos
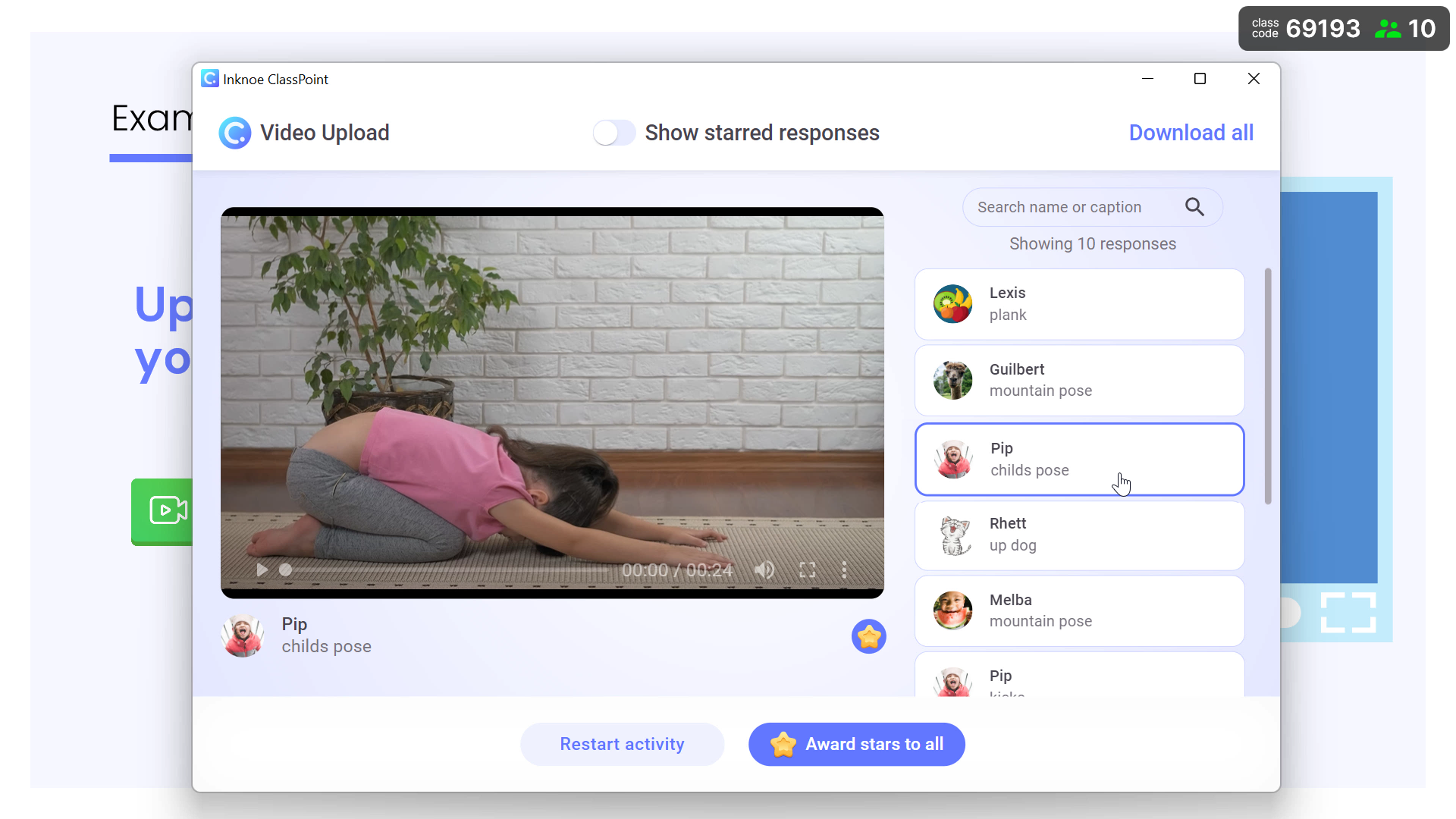
Educational videos can serve as powerful tools for modeling behaviors, techniques, and concepts that students can observe and imitate.
How you can do it: Integrate videos into your lessons that show experts demonstrating skills or explaining concepts. Encourage students to watch these videos and discuss what they observed, asking them to identify key points and techniques.
How it helps: Videos provide visual and auditory examples of how to perform tasks or understand concepts, catering to different learning styles. They can be paused and replayed, allowing students to review and reinforce their learning at their own pace.
One of the top-of-mind-tools when video assessments are put into talks is Microsoft Flip. With recent announcement of plans to sunset, we've come up with a guide to walk you through how ClassPoint serves as a good alternative.
6. Peer Review and Feedback Sessions
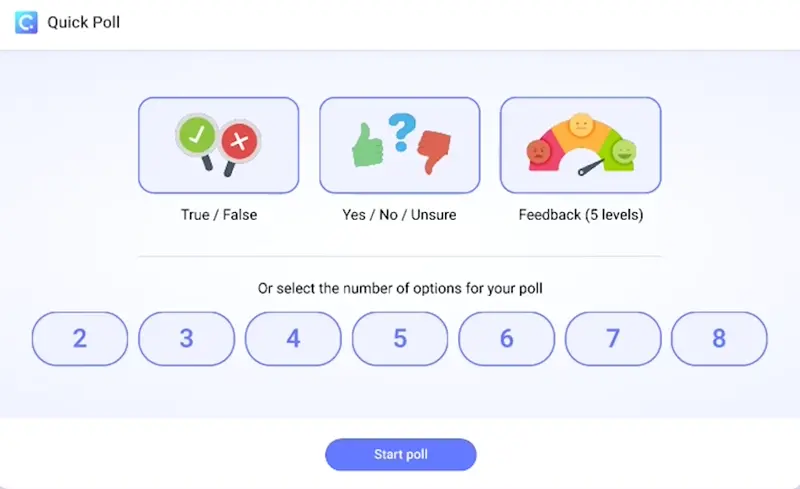
Peer review involves students reviewing each other’s work and providing constructive feedback, which promotes critical thinking and observational learning.
Here's our ultimate cheat sheet on how you can make use of ClassPoint in a ton of ways including brainstorming sessions and peer discussions.
How you can do it: Collective feedback using a quick poll. Or organize sessions where students exchange assignments and provide feedback on each other’s work. Provide guidelines and criteria to help them give constructive and meaningful feedback.
How it helps: Peer review encourages students to critically evaluate work, both their own and others’. This process enhances their analytical skills and helps them learn to accept and give constructive criticism, fostering a growth mindset.
7. Collaborative Technology Platforms
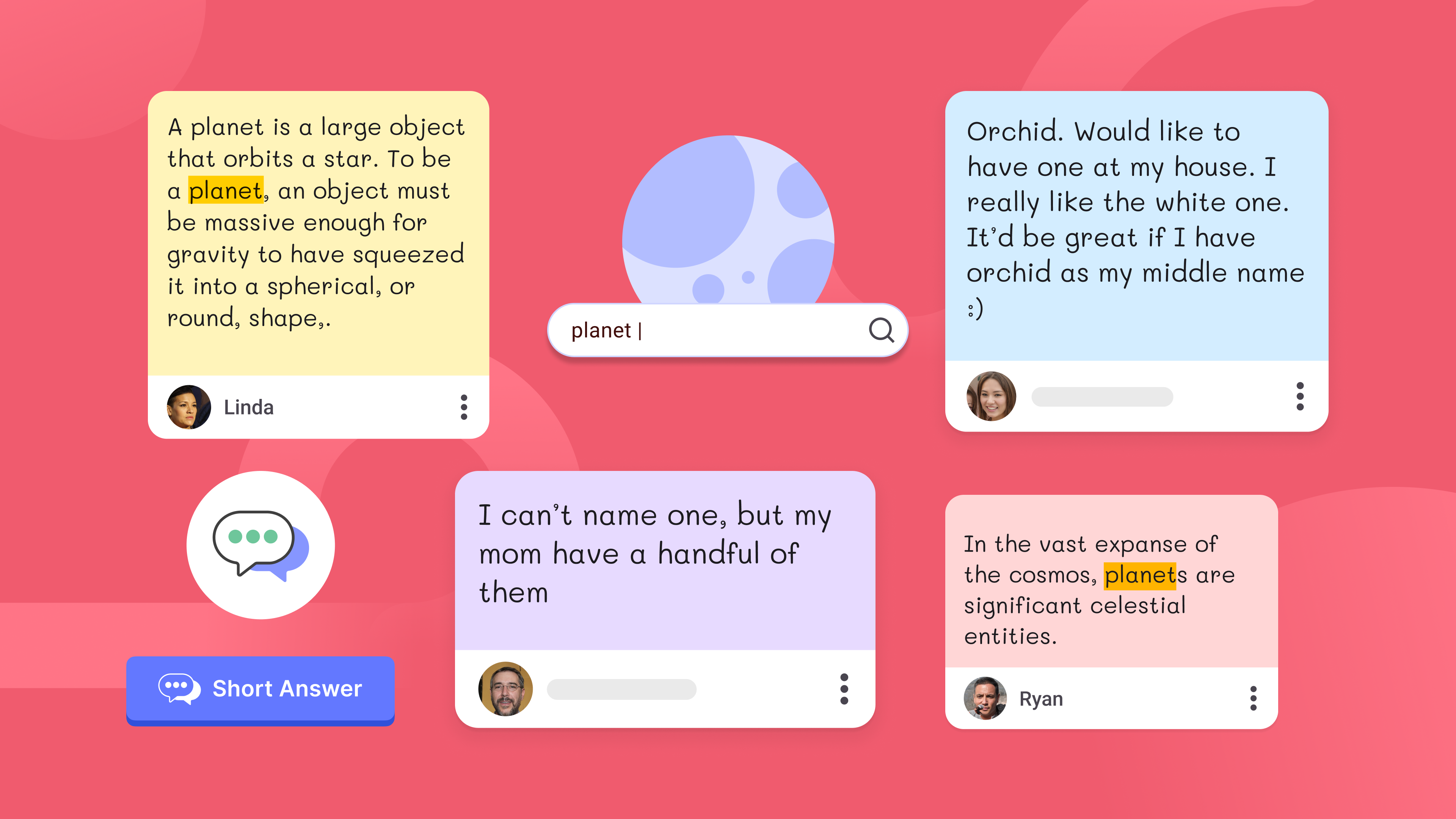
Collaborative technology platforms facilitate group work and peer interaction, enhancing social learning through digital means.
How you can do it: Use tools like Google Docs, Padlet, or educational apps that allow real-time collaboration on projects and assignments. Set clear goals and monitor progress, providing feedback and support as needed.
Real-time submissions and review? ClassPoint is your best bet. With a slew of quizzes and interactive presentation tools, tied in with gamification, you won't ever have to learn how to use an unfamiliar tool as ClassPoint is directly embedded into a presentation app we all love, PowerPoint.
How it helps: These platforms enable students to work together seamlessly, regardless of physical location. They promote collaboration, communication, and the sharing of ideas, preparing students for the digital work environment.
8. Real-Life Case Studies and Discussions
Analyzing real-life scenarios helps students apply theoretical concepts to practical situations and learn from real-world examples.
How you can do it: Incorporate case studies relevant to your subject into lessons. Facilitate discussions where students can analyze and debate different aspects of the case, applying their knowledge to solve problems.
How it helps: Case studies bridge the gap between theory and practice, making learning more relevant and engaging. They develop students’ analytical, problem-solving, and decision-making skills by applying concepts to real-world situations.
9. Classroom Management Techniques
Implementing classroom management strategies that model positive behaviors and social interactions can enhance social learning.
How you can do it: Demonstrate respectful communication, active listening, and conflict resolution skills in your interactions with students. Establish clear rules and expectations, and consistently model the behaviors you expect from students.
How it helps: Students learn by observing the teacher’s behavior and how conflicts are resolved. This modeling helps create a positive classroom environment where students feel respected and valued, promoting better social interactions and cooperation.
Overwhelmed with all the available strategies you still have yet to try? Fret not - we get you covered with our comprehensive guide on bulletproof classroom management strategies.
10. Gamified Learning Activities

Gamified learning activities involve using game-based elements to make learning more engaging and interactive, encouraging observation and imitation in a fun context.
How you can do it: Incorporate educational games, quizzes, and simulations that require teamwork and strategy. Use leaderboards, stars, and rewards to motivate students and create a sense of competition.
How it helps: Gamification makes learning enjoyable and motivating. It encourages students to engage with the material actively, collaborate with peers, and apply their knowledge in a game setting, reinforcing learning through practice and interaction.
Learn more about game-based learning here.
Best Practices for Implementing Social Learning Theory in the Classroom
To effectively apply social learning theory in your classroom, consider these best practices:
🌟 Foster a Positive Environment: Encourage respect, cooperation, and open communication to create a supportive atmosphere.
👩🏫 Model Desired Behaviors: Demonstrate the behaviors and skills you want students to learn consistently.
🤝 Promote Collaboration: Design tasks that require group work and peer interaction to enhance learning through social engagement.
📝 Use Constructive Feedback: Provide timely and specific feedback to guide student learning and improvement.
💻 Integrate Technology: Use collaborative platforms and educational tools to support and enhance social learning opportunities.
🔍 Encourage Reflection: Promote reflective practices such as journals and discussions to help students analyze their learning experiences.
Food for Thought
Social learning theory offers a powerful framework for transforming educational practices, emphasizing the importance of observation, interaction, and modeling in the learning process. By integrating these principles in 21st century classrooms, educators can foster a more engaging and collaborative environment that supports both academic and personal growth for students.
The true strength of social learning lies in its ability to connect learners with real-world experiences and diverse perspectives. By cultivating an atmosphere where students learn from each other and their surroundings, we can inspire a generation of critical thinkers and proactive learners ready to thrive in an ever-changing world.
